The diagnostic accuracy of pericardial and urinary lipoarabinomannan (LAM) assays in patients with suspected tuberculous pericarditis
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
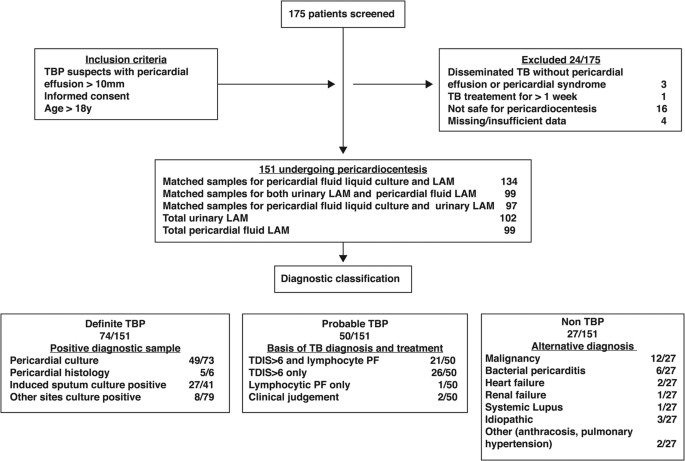
We evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of urinary and pericardial fluid (PF) lipoarabinomannan (LAM) assays in tuberculous pericarditis (TBP). From October 2009 through September 2012, 151
patients with TBP were enrolled. Mycobacterium tuberculosis culture and/or pericardial histology were the reference standard for definite TBP. 49% (74/151), 33.1% (50/151) and 17.9% (27/151)
of patients had definite-, probable-, and non-TB respectively; 69.5% (105/151) were HIV positive. LAM ELISA had the following sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio, negative
likelihood ratio, positive predictive value and negative predictive values (95% confidence interval): urinary - 17.4% (9.1–30.7), 93.8% (71.7–98.9), 2.8 (0.1–63.3), 0.9 (0.8–0.9), 88.9%
(56.5–98.0), and 28.3% (17.9–41.6); PF - 11.6% (6.0–21.3), 88% (70.0–95.8), 0.9 (0.08–12.0), 1.0 (0.9–1.1), 72.7% (43.4–90.1), and 26.6% (18.2–36.9). Sensitivity increased with a CD4 ≤ 100
cells/mm3 from 3.5% to 50% (p