Fe-mil-101 exhibits selective cytotoxicity and inhibition of angiogenesis in ovarian cancer cells via downregulation of mmp
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Though metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have inspired potential applications in biomedicine, cytotoxicity studies of MOFs have been relatively rare. Here we demonstrate for the first
time that an easily available MOF, Fe-MIL-101, possesses intrinsic activity against human SKOV3 ovarian cancer cells and suppress the proliferation of SKOV3 cells (IC50 = 23.6 μg mL−1) and
normal mouse embryonic fibroblasts (BABL-3T3, IC50 = 78.3 μg mL−1) cells. It was more effective against SKOV3 cells than typical anticancer drugs such as artesunate (ART, IC50 = 96.9 μg
mL−1) and oxaliplatin (OXA, IC50 = 64.4 μg mL−1), but had less effect on normal BABL-3T3 cells compared with ART (IC50 = 36.6 μg mL−1) and OXA (IC50 = 13.8 μg mL−1). Fe-MIL-101 induced
apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) via G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and decreased the mitochondrial membrane potential in HUVECs and induced apoptosis. Furthermore,
Fe-MIL-101 exhibited stronger antiangiogenic effects in HUVEC cells than antiangiogenic inhibitor (SU5416) via downregulation the expression of MMP-2/9. Our results reveal a new role of
Fe-MIL-101 as a novel, non-toxic anti-angiogenic agent that restricted ovarian tumour growth. These findings could open a new avenue of using MOFs as potential therapeutics in
angiogenesis-dependent diseases, including ovarian cancer. SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS DESIGN, SYNTHESIS AND EVALUATION OF NOVEL TETRAHYDROPYRIDOTHIENOPYRIMIDIN-UREAS AS CYTOTOXIC
AND ANTI-ANGIOGENIC AGENTS Article Open access 11 June 2022 DISCOVERY OF 1-(5-BROMOPYRAZIN-2-YL)-1-[3-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)BENZYL]UREA AS A PROMISING ANTICANCER DRUG VIA SYNTHESIS,
CHARACTERIZATION, BIOLOGICAL SCREENING, AND COMPUTATIONAL STUDIES Article Open access 20 December 2023 ENHANCED ANTI-ANGIOGENIC EFFECTS OF APREPITANT-LOADED NANOPARTICLES IN HUMAN UMBILICAL
VEIN ENDOTHELIAL CELLS Article Open access 27 August 2024 INTRODUCTION Ovarian cancer is the second most common gynaecological malignancy worldwide and the leading cause of death among
gynaecologic neoplasms. The tumour microenvironment encompasses various stromal cells and extracellular matrix surrounding tumour cells and differs from the normal tissue environment1.
Increasing evidence suggests that the tumour microenvironment also plays critical roles in tumour progression and metastasis, and new strategies for synergistic tumour therapeutics target
both tumour microenvironment and tumour cells1. The tumour microenvironment comprises numerous signalling molecules and pathways that influence the angiogenic response2. Angiogenesis, the
formation of new blood vessels from a pre-existing vascular network, is principally mediated by endothelial cell proliferation and migration. It provides oxygen and nutrients to actively
proliferating tumour cells3, and is responsible for the development and metastasis of most types of tumours4. The pathogenesis of malignant tumours is mainly caused by the disruption of
angiogenesis and the imbalanced endothelial remodelling and regression. Therefore, inhibition of angiogenesis is emerging as a promising new approach for cancer treatment5,6,7,8,9. Matrix
metalloproteinases (MMP), a family of zinc-binding proteins including the gelatinases MMP-2 and MMP-9, have been shown to play a central role in angiogenesis and tumour cell invasion and
metastasis due to their ability to degrade the extracellular matrix10. Thus, downregulating MMP-2/9 expression or decreasing enzymatic activities in the tumour microenvironment is crucial in
inhibiting angiogenesis, tumour invasion and metastasis1. As a result, MMP inhibitors have been recognized as drug candidates for anticancer therapeutics, and much effort has been made to
design and develop molecules that inhibit MMP activity5,10. In contrast to conventional approaches, nanotechnology presents novel opportunities to develop promising diagnostics and
therapeutics tools for the treatment of cancer and many other diseases11,12. However, little evidence exists that nanomaterials themselves might possess intrinsic anticancer properties, and
only a few nanoparticles’ intimate interactions with the tumour microenvironment were reported13,14,15,16,17. For example, Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with piroctone olamine18,
fullerene-based nanomaterial Gd@C82(OH)2219,20,21,22, hollow mesoporous carbon nanocapsules (HMCNs)23 and polysaccharide-based hydrogels24 have been found to exhibit inhibition of MMP
activity. However, none have translated to clinical application due to the dose-limiting side effects following systemic administration of these pharmacological MMP inhibitors24. Compared
with nanostructures such as metallic-, dielectric-, magnetic-, liposomal-, and carbon-based structures with potential medical applications, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are currently
eliciting much attention in materials science and biotechnology due to outstanding properties including crystalline open structures, extremely high surface areas, tunable pores, diverse
structure and chemical functionality25,26. For instance, Fe-MIL-101_NH2, consisting of trimeric iron(III) octahedral clusters interconnected by 1,4-benzenedicarboxylate anions, has been
reported as a nontoxic nanocarrier for the controlled delivery of several antitumoural and retroviral drugs27,28. Until now, the available toxicity information regarding MOFs have remained
scarce and the contemporary use of MOFs for cancer treatment has been largely limited to serving as contrast agents for imaging techniques and carriers for drug delivery28,29,30,31,32. Few
reports have directly used MOFs as anticancer agents. Treating malignant tumours effectively with low toxicity remains a major challenge and is urgently required. Despite the intensive
studies on the synthesis, characterization and possible applications, the biocompatibility and cytotoxicity of MOFs have rarely been investigated. Until now, the available toxicity
information dealing with MOFs or coordination polymers has been limited33. For instance, the toxicological effects of three different iron carboxylate MOFs, MIL88A (fumarate), MIL88B
(tetramethylterephthalate) and MIL100 (trimesate), was examined by Horcajada and colleagues both _in vitro_ and _in vivo_34, and all three showed no observable toxicity. A recent study
reported that these iron carboxylate MOFs were rapidly sequestered by the liver and spleen, biodegraded and directly eliminated through the urine or faeces without causing obvious
toxicity35. The values of the half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) for the MIL-101_NH2BrBODIPY,1,3,5,7-tetramethyl-4,4-difluoro-8-bromomethyl-4-bora-3a,4a-diaza-_s_-indacene
(BrBODIPY) coated MIL-101 on human HT-29 colon adenocarcinoma cells have also been reported36. Additionally, the _in vitro_ toxicity of lanthanide-based MOFs was carried out in HT-29 and
acute lymphoblastic leukaemia human cells, showing important cytotoxicity values28,37. Zinc MOFs exhibited a time and concentration dependent cytotoxicity in rat PC12 pheochromocytoma
cells38. The CuBTC MOF associated drug 5-fluorouracil was extremely cytotoxic against human MCF-7 breast cancer adenocarcinoma cells and human HL60 acute promyelocytic leukaemia cells via
apoptosis mechanisms39. The mechanisms of apoptosis induced by MOFs are largely unknown. Moreover, little is known about the interactions of MOFs with the tumour microenvironment, and the
antiangiogenic properties and inhibition of MMPs of MOFs remain almost completely unknown. Therefore, more research is needed regarding the use of MOFs in cancer therapy applications. Here
we investigated the inhibitory effects of Fe-MIL-101 on SKOV3 human ovarian cancer, HeLa cervical cancer and A549 lung cancer cell line growth and the proliferation, migration and tube
formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). We also studied the effect of Fe-MIL-101 on cell apoptosis and MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression in HUVECs and SKOV3 cells. This study
evaluated the mechanism associated with the antitumour and antiangiogenic activity of Fe-MIL-101. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION CHARACTERIZATION OF FE-MIL-101 Fe-MIL-101 was obtained from ferric
hydroxide and terephthalic acid as previously described25. The textural properties of Fe-MIL-101 are summarized in the supplementary Table S1 and Fig. S1. The adsorption/desorption isotherm
of Fe-MIL-101 is of type I indicating the presence of the microporous network, which possesses the Langmuir surface area (5400 m2g−1) and Brunauer–Emmer–Teller (BET) surface area (3710
m2g−1). The X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of Fe-MIL-101 is also shown in supplementary Fig. S2. The diffraction peaks all corresponded to the product synthesized by Skobelev. Together
these results confirmed the proper synthesis of Fe-MIL-101. EFFECT OF FE-MIL-101 ON CELL GROWTH The cytotoxicity of Fe-MIL-101 in four cell lines (HeLa, A549, SKOV3 and HUVEC cells) and
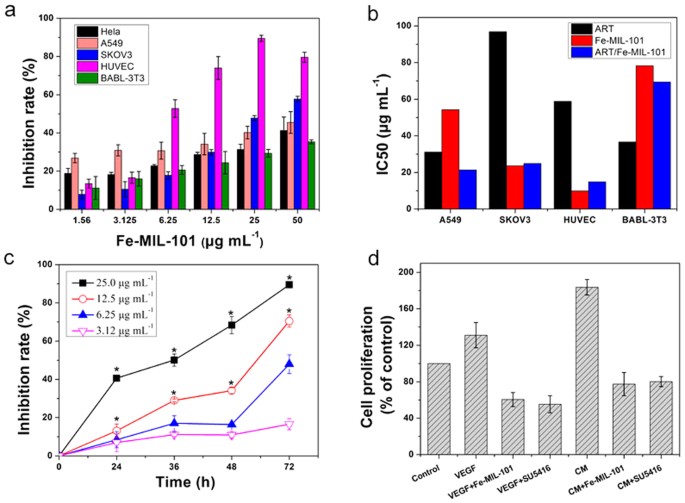
control normal mouse embryonic fibroblast BABL-3T3 cells was evaluated by the MTT assay. Fe-MIL-101 exhibited concentration-dependent inhibition in HeLa, A549, SKOV3, HUVEC and BABL-3T3
cells with a half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 41.9, 74.6, 56.5, 33.5, and 91.2 μg mL−1 at 24 h, respectively (Table 1 and Fig. 1a). The IC50 for A549 cells was the highest
among these cancer cells. These data show that Fe-MIL-101 is least active against A549 cells than other cells and demonstrate that Fe-MIL-101 has selective toxicity against different cancer
cell lines. Fe-MIL-101 also possessed cytotoxicity in a time-dependent manner in all cells except for HeLa and BABL-3T3 cells. The IC50 for A549, SKOV3 and HUVEC cells was reduced to 68.5,
37.3, and 24.5 μg mL−1, respectively, when treated with Fe-MIL-101 for 48 h. When treatment time was prolonged to 72 h, the IC50 value for A549, SKOV3 and HUVEC cells was 54.3, 23.6, and 9.9
μg mL−1, respectively, which was much lower than the values at 24 and 48 h. Differential cytotoxicity is important because one of the greatest challenges facing chemotherapy is the
inability of anticancer drugs to effectively distinguish between tumour cells and normal cells40. The IC50 of Fe-MIL-101 in BABL-3T3 cells was approximately 3.3- and 8-fold higher than that
for SKOV3 cells and HUVEC cells, respectively. Fe-MIL-101 also has selective toxicity against HeLa, A549, and SKOV3 cancer cells and HUVEC cells and shows less toxicity against normal
BABL-3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblasts cells (Fig. 1a). This suggests that Fe-MIL-101 may have a potential utility in the selective treatment of cancer cells. Other Fe based MOFs, MIL-100 and
MIL-88B, were also used to treat SKOV3 cells (Table 1). Fe-MIL-101 was more active against SKOV3 cells than Fe-MIL-100 and Fe-MIL-88B. Other Fe-based MOFs34 including MIL-100, MIL101_2CH3,
MIL101_NH2, MIL88B and derivations (supplementary Table S2) exhibited low toxicity on HeLa cells with IC50 values ranging from 690 to 2500 μg mL−1. These values are much higher than that of
Fe-MIL-101 (IC50 = 41.9 μg mL−1), indicating that the structure of iron terephthalic acid may play an important role. Therefore, the roles of Fe3+ and organic ligand (terephthalic acid,
H2BDC) were also tested _in vitro_. The organic constitutive linker H2BDC was not toxic on HeLa cells with IC50 values 800 ± 20 μg mL−134. In our study, the IC50 value of H2BDC for 24 h for
SKOV3, BABL-3T3, and HeLa cells was 1353.9, 1111.6 and 1166.8 μg mL−1, respectively, suggesting that the organic linker H2BDC was not toxic. Iron is a component in haemoglobin and exists at
approximately 22 μM in blood plasma, and shows little toxicity in the body41. Iron oxide nanoparticles are clinically approved as magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents, and _in vitro_
assays have shown that these particles do not exhibit toxicity34. We also observed that the IC50 value of FeCl3•6H2O was above 1000 μg mL−1 for the above three mentioned cell lines. We also
investigated the concentration of iron released from Fe-MIL-101 into medium by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry ICP-AES measurement. No detectable iron leaked into the
medium at 37 °C after 72 h. These results suggest that Fe-MIL-101 instead of Fe3+ or organic ligand play key roles in cytotoxic activity and show that Fe-MIL-101 exhibited much higher
cytotoxic activity against SKOV3 cells than other iron MOFs such as Fe-MIL-100 and Fe-MIL-88B (supplementary Table S2). Other MOFs such as Tb-MOFs35 showed high cytotoxicity values against
human HT-29 colon adenocarcinoma cells (IC50~10 μg mL−1) and Gd-MOFs28 also showed high cytotoxicity values against human acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells (IC50~15 μg mL−1), which was due
to the linkers’ antitumoural activity34. By contrast, the cytotoxicity of ZrMOFs UiO6634 (IC50 HeLa = 400 μg mL−1) is much lower than that of Fe-MIL-101. Interestingly, Fe-MIL-101 exhibited
higher cytotoxicity against SKOV3 cells than the anticancer drug carboplatin, for which IC50 is 54.6 μg mL−1 at 72 h42. Even compared with the positive controls artesunate (ART) and
oxaliplatin (OXA), the inhibitory activity of Fe-MIL-101 was more effective than ART and OXA against SKOV3 and HUVEC cells, but only had a minor effect on HeLa, A549 and BABL-3T3 cells. To
achieve better anti-cancer effects, Fe-MIL-101 was used as carrier matrices for the ART delivery system. The amount of the drug laden in Fe-MIL-101 was measured by UV-vis spectroscopy and
the ART contents were determined to be 0.70 g of ART per gram of the sample of Fe-MIL-101 (0.7 g/g material). Cytotoxic tests of ART/Fe-MIL-101 were also carried out against A549, SKOV3,
HUVEC and BABL-3T3 cell lines (Table 1 and Fig. 1b). As shown in Fig. 1b, the IC50 values of ART were higher than that of ART/Fe-MIL-101 for A549, SKOV3 and HUVEC cells, suggesting that
ART/Fe-MIL-101 exhibits better anti-proliferative effects than ART. However, except for A549 cells, the IC50 values of ART/Fe-MIL-101 on cells were similar to those of Fe-MIL-101 under the
same condition. This implies that there is no significant difference between Fe-MIL-101 and ART/Fe-MIL-101. This could be attributed to the following reasons: the adsorption of ART led to a
significant decrease in both surface areas, and pore volumes of Fe-MIL-101 indicated that ART was mainly adsorbed within the pores instead of on the external surface of Fe-MIL-101, whereas
surface areas decrease from 3700 m2g−1 to 1760 m2g−1 and pore volumes decrease from 1.96 cm3g−1 to 0.93 cm3g−1 (Table S1, supplementary Fig. S3). Therefore, Fe-MIL-101 with very high
cytotoxicity would contact SKOV3 cells first and cause cell death before the slow release of ART. The above results again confirm that Fe-MIL-101 is the major cause of cytotoxic activity in
cancer and normal cells during this treatment time. More research is needed to obtain further insight into the reason why ART/Fe-MIL-101 did not enhance toxic effects compared with unloaded
Fe-MIL-101. To further evaluate the cytotoxic effect of the Doxorubicin (DOX) and DOX/Fe-MIL-101 in three cancer cell lines (HeLa, A549, and SKOV3 cells) and control normal mouse embryonic
fibroblast BABL-3T3 cells by the MTT assay. As shown in supplementary Table S3, free DOX and DOX/Fe-MIL-101 also possessed cytotoxicity in a time-dependent manner in all cells. When
treatment time was prolonged to 72 h, both free DOX and DOX/Fe-MIL-101 gave approximate IC50, indicating DOX/Fe-MIL-101 has similar cytotoxic effects against HeLa, A549, and SKOV3 cells than
free DOX. However, the IC50 values of DOX/Fe-MIL-101 were higher than that of DOX for the normal cells, suggesting DOX/Fe-MIL-101 also shows less toxicity against normal BABL-3T3 mouse
embryonic fibroblasts cells. This selective toxicity was consistent with Fe-MIL-101. Endothelial cells are the main component of new capillary vessels, and endothelial cell proliferation
plays a critical role in the formation of new capillaries43. As proliferation, migration and capillary tube formation of endothelial cells are critical steps in angiogenesis44, we
investigated the effects of Fe-MIL-101 on the proliferation of HUVECs. As illustrated in Fig. 1c, treatment with Fe-MIL-101 (3.12–25 μg mL−1) for 24, 36, 48 and 72 h resulted in inhibition
of cell proliferation in a concentration-dependent and time-dependent manner. The inhibitory rates of HUVEC proliferation at 24, 36, 48 h and 72 h were 40.6 ± 1.5%, 50.1 ± 3.2%, 68.4 ± 4.4%
and 89.4 ± 1.6% for 25 μg mL−1 Fe-MIL-101, respectively. There were significant differences in concentrations higher than 6.25 μg mL−1 (*_P_ < 0.01) (Fig. 1c). Previous studies
demonstrated that ART exhibits anti-proliferation and anti-angiogenic activity as well as antitumour activity45. Interestingly, similar to the cytotoxicity study of Fe-MIL-101 and
ART/Fe-MIL-101, Fe-MIL-101 was more effective than ART in inhibiting cell growth, and loading ART did not improve the cytotoxicity effect. THE EFFECT OF FE-MIL-101 ON HUVEC PROLIFERATION IN
CONDITIONED MEDIA (CM) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) plays various functions in endothelial cells, including the induction of proliferation and differentiation46. VEGF increased
the proliferation of HUVECs compared with controls (Fig. 1d). Moreover, CM from SKOV3 cells induced a significant increase in the proliferation of HUVECs to levels higher than treatment with
VEGF. However, Fe-MIL-101 significantly inhibited cell proliferation under VEGF and CM treatment conditions. Furthermore, Fe-MIL-101 displayed a similar anti-proliferation effect compared
with SU5416, a selective inhibitor of VEGF tyrosine kinase activity. FE-MIL-101 INDUCES APOPTOSIS OF HUVECS To determine the underlying mechanism of Fe-MIL-101 activity, the nuclear
morphology of control and Fe-MIL-101 treated cells was observed by staining cell nuclei with Hoechst 33342 as previously described47. Apoptotic cells are generally characterized by
condensation of chromatin and/or nuclear fragmentation. HUVEC cells were cultured and exposed to Fe-MIL-101 at concentrations of 12.5 and 25 μg mL−1 for 48 h. As shown in Fig. 2a, control
cells, which were uniformly blue, were viable, whereas treated cells showed apoptosis, with nuclear shrinkage, chromatin condensation and cytoplasmic blebbing, and bright blue dots in the
nuclei, representing nuclear fragmentation. The FITC-Annexin-V and PI binding assay was used to further confirm Fe-MIL-101-induced apoptosis (Fig. 2b). In the dual parametric dot plots, the
lower left quadrant represents the viable cell population (Annexin-V negative and PI negative), the upper right represents apoptotic cells undergoing secondary necrosis at the last stage or
dead cells (Annexin-V and PI double positive), and the lower right represents the early stage apoptotic cell population (Annexin-V positive and PI negative). As the concentration of
Fe-MIL-101 increased from 3.12–25 μg mL−1, the Annexin-V positive/PI negative cells increased from 3.7% to 13.7%, whereas the double positive cells increased from 17.4% to 40.2%. Increasing
numbers of apoptotic cells progressed from the early stage to the late stage resulting in either death or secondary necrosis under Fe-MIL-101 at higher concentrations. This data confirms
again that Fe-MIL-101 can effectively induce the apoptosis of HUVECs. FE-MIL-101 DECREASES MITOCHONDRIAL MEMBRANE POTENTIAL OF HUVECS Mitochondria play a key role in the apoptotic pathway of
cell death and changes in mitochondrial membrane permeability comprise the early events during apoptosis48. Mitochondrial membrane potential was measured using JC1 (5, 5′, 6,
6′-tetrachloro-1, 1′, 3, 3′-tetraethyl-imidacarbocyanine iodide) staining. Treatment of HUVEC cells with Fe-MIL-101 resulted in increased JC1 green fluorescence, indicating a decrease of
mitochondrial membrane potential (Fig. 2c). These results indicate that Fe-MIL-101 induced apoptosis in HUVEC cells through the mitochondrial pathway. The adverse changes in mitochondrial
function due to Fe-MIL-101, with possible association of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, trigger the apoptosis process49. Fen+ ions can generate ROS through the
Fenton or Haber–Weiss reaction when in contact with cells34,50. It is noteworthy that redox active metals and ROS pathways alter the plasma membrane potential, provoking changes in cell
cycle regulation51, or causing the membrane lipid peroxidation52, resulting in cellular death or apoptosis34. FE-MIL-101 INDUCES G0/G1 PHASE CELL CYCLE ARREST IN HUVEC CELLS The cell cycle
is an important key step in angiogenesis53,54. We next performed flow cytometry to analyse the effects of Fe-MIL-101 on the cell cycle. Analysis of the cell cycle distribution of HUVEC cells
indicated that Fe-MIL-101 treatment induced an increase in the percentage of G0/G1 phase cells and a reciprocal reduction in the percentage of S and G2/M phase cells (Table 2, Fig. 2d).
Treatment with Fe-MIL-101 for 48 h led to a dose-dependent accumulation of cells in G0/G1 phase (64.5% in control cells versus 53.9% in cells treated with 25 μg mL−1 Fe-MIL-101; _P_ <
0.05) and a decrease in the number of cells in S phase (_P_ < 0.05) and G2/M phase (_P_ < 0.05). We next evaluated apoptosis levels by flow cytometric Annexin V/PI assay. The results
showed that 48 h incubation of cells with 3.12–25.0 μg mL−1 Fe-MIL-101 resulted in 21.1–53.9% apoptotic populations (Table 2), indicating that the apoptosis rate significantly increased with
the increase of Fe-MIL-101 concentration (Fig. 2b). These data show that Fe-MIL-101 induced apoptosis on HUVECs via G0/G1 cell cycle arrest similar to nanoparticles such as
[Gd@C82(OH)22]n54, gold nanoparticles (AuNP40)55, SDS-solubilized single-walled carbon nanotubes (SDS-SWCNTs)56 and silica nanoparticles57. For example, [Gd@C82(OH)22]n treatment of human
MCF-7 breast cancer cells and human ECV304 umbilical vein endothelial cells induced G0/G1 phase arrest and induced cell apoptosis by downregulating CDK4, CDK6, cyclin E, cyclin D2, and Bcl-2
expressions and by upregulating p21 and Bax expressions54. AuNPs induced cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase and induced apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells55. SDS-SWCNTs caused cell cycle
arrest at G0/G1 phase in normal rat NRK 52E kidney tubular cells56. Silica nanoparticles induced G1 phase arrest through upregulation of p53 and p21 in the rat embryonic ventricular
myocardial cell line H9c2(2-1)57. The effect of Fe-MIL-101on normal BABL-3T3 cells was also examined by flow cytometry for comparison. The results were shown in supplementary Fig. S4. The
cell was mainly distributed G0/G1 phase (76%) in control cells by flow cytometry analysis. Treatment with different concentration of Fe-MIL-101 for 48 h not led to a change in G0/G1 phase.
As well as Fe-MIL-101 has no effect on the distribution of cell S phase and G2/M phase, suggesting Fe-MIL-101 did not disrupt the cell cycle of normal cells. However, Fe-MIL-101 treatment
induced an increase in the percentage of G0/G1 phase and a reciprocal reduction in the percentage of S and G2/M phase in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Above results
indicated that Fe-MIL-101 effectively induced HUVECs arrest at G0/G1 phase, but did not disrupt the cell cycle of normal cells, which maybe the cause of selectivity toxicity towards cancer
cells but not the normal cells. EFFECTS OF FE-MIL-101 ON MIGRATION OF HUVECS The migration of endothelial cells is an important step of angiogenesis. We performed wound-healing experiments
and measured the amount of migrating cells to the wound area after HUVEC cells were treated with 12.5 μg mL−1 of Fe-MIL-101. ART, which inhibits migration of HUVECs45, served as a positive
control (Fig. 3a). The migrating number of cells treated by Fe-MIL-101 was less than those treated with ART and the controls (Fig. 3b). In addition, Fe-MIL-101 inhibited HUVEC migration in a
time-dependent manner. This effect was not due to cell death, because HUVECs did not show any morphological changes such as blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin
condensation or chromosomal DNA fragmentation. HUVEC proliferation was also determined by MTT assay. Figure 1c shows that the inhibition rate was about 13.1% when HUVEC cells were treated
with 12.5 μg mL−1 Fe-MIL-101 for 24 h, indicating that this concentration of Fe-MIL-101 was non-toxic over a short period and the inhibition of cell migration was not caused by the
cytotoxicity of Fe-MIL-101. Together this indicates that Fe-MIL-101 possessed a stronger inhibitory effect on migration than control and ART groups, and this inhibitory effect was not due to
the cytotoxicity of Fe-MIL-101. Fe-MIL-101 also inhibited SKOV3 cell migration in a time- and dose-dependent manner (supplementary Fig. S4). This suggests that Fe-MIL-101 has the potential
to inhibit tumour and endothelial cell migration. EFFECTS OF FE-MIL-101 ON HUVEC TUBE FORMATION Tumour growth and proliferation depends on the formation of new blood vessels (vasculogenesis
and angiogenesis) for the supply of oxygen and nutrients. VEGF induced endothelial cell morphogenic differentiation into capillary-like structures58 and CM collected from tumour cells
increased endothelial cell proliferation, migration and tube-like structure formation _in vitro_59. Therefore, we assessed the effect of Fe-MIL-101 on new blood vessel formation _in vitro_
of HUVECs treated with 10 ng mL−1 VEGF or CM collected from SKOV3 cells. As shown in Fig. 4a, HUVECs formed a robust and complete tube network within 12 h post-seeding. Tube formation of
HUVEC was observed in all groups. The tubes of the CM treated group were longer than the VEGF treated group, which may be because CM contains some pro-angiogenic proteins, such as VEGFs,
angiopoietin-2 and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF)60. Fe-MIL-101 (12.5 μg mL−1) partially abolished this process with an observed reduction of number and length of tube-like
structures. Capillary tubes were completely disassembled in the presence of 25 μg mL−1 Fe-MIL-101. There was an approximately 60–90% reduction in the total tube length per field following
12.5 and 25 μg mL−1 Fe-MIL-101 treatment for 12 h (Fig. 4b,c), suggesting a decrease in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, Fe-MIL-101 also had better antiangiogenic activity compared with
the inhibitor SU5416 (20 μM). As shown in Fig. 4b, the length of tubes induced by 25 μg mL−1 Fe -MIL-101 was approximately three-fold shorter than that induced by SU5416 in the VEGF group
and about 5.5-fold shorter than the length of tubes induced by SU5416 in the CM group. Similar results were observed in the group pre-treated with 25 μg mL−1 Fe-MIL-101 (Fig. 5a–c). In the
presence of VEGF, tube formation was inhibited by 93%, which showed a comparable effect in the presence of CM. AgNPs9 (80 μg mL−1) inhibited about 80% tube formation of bovine retinal
endothelial cells on Matrigel. HMCNs23 effectively inhibited the formation of tubes induced by VEGF. Based on the inhibition percentage equation, Fe-MIL-101 inhibited more than 90% tube
formation of HUVECs (Figs 4c and 5c), suggesting that Fe-MIL-101 exhibited better antiangiogenic activity compared with AgNPs and HMCNs. These data show that Fe-MIL-101 could serve as a
potential candidate for anti-angiogenic therapy. EXPRESSION OF MMP-2 AND MMP-9 IN SKOV3 AND HUVEC CELLS MMPs appear to play an important role in the process of tumour progression and
angiogenesis of endothelial cells. Thus, we investigated MMP-2/9 protein expression in SKOV3 and HUVEC cells. MMPs are secreted as pro-enzymes that become active when cleaved. Western blot
analysis showed that the total protein expression of MMP-2 (MMP-2 and active-MMP-2) and MMP-9 markedly decreased in SKOV3 cells upon Fe-MIL-101 treatment in a dose-dependent manner (Fig.
6a). Analyses of MMPs in HUVECs showed that VEGF and CM can upregulate the expression of MMP-2, MMP-9 and their active forms (Fig. 6b,c). These results are consistent with previous
studies61,62. It is also interesting to note that treatment with Fe-MIL-101 significantly inhibited VEGF or CM-induced upregulation of MMP expression and activities. Moreover, MMP-2/9 levels
in SKOV3 cells were significantly diminished in a dose-dependent manner upon treatment with Fe-MIL-101 for 24 h. Recent studies have shown that MMP-2 and MMP-9 are critical in the
progression of angiogenesis. For example, the fullerene-based nanoparticle Gd@C82(OH)22 and hollow mesoporous carbon nanocapsules (HMCNs) serve as potent antiangiogenesis inhibitors through
downregulating multiple angiogenic factors including MMP-2/921,23. Compared with Gd@C82(OH)22, HMCN nanoparticles, the synthesis of Fe-MIL-101 is more simple. Moreover, Fe-MIL-101 possesses
better activity of inhibition of MMP-2/9 than HMCN nanoparticles. Together the above results reveal that proliferation and migration of tumour cells and HUVECs were inhibited in the presence
of Fe-MIL-101. Numerous gene products including urinary plasminogen activator, matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2, MMP-9) and cyclooxygenase 2 and other chemokines regulate cell migration,
invasion and tube formation processes63. Our results show that the expressions of MMP-2 and MMP-9 proteins in SKOV3 and HUVEC cells incubated with Fe-MIL-101 are significantly downregulated
in a concentration-dependent manner, suggesting that Fe-MIL-101 exhibits significant inhibitory effect on the metastasis of metastatic cancer cells by downregulating the expressions of
metastasis-related proteins. CONCLUSIONS Fe-MIL-101 was found to elicit anti-proliferative effect on HeLa, A549, SKOV3 cancer cells and HUVECs and showed less toxicity against BABL-3T3
normal mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. Fe-MIL-101 may have a potential utility to distinguish effectively between HeLa, A549, SKOV3 tumour cells and normal cells. Moreover, Fe-MIL-101
effectively induced apoptosis of HUVECs through the mitochondrial pathway and caused G0/G1 cell cycle arrest, but has no effect on cell cycle of normal BABL-3T3 cells. In addition,
Fe-MIL-101 suppressed angiogenesis processes _in vitro_. Fe-MIL-101 has the potential to inhibit tumour and endothelial cell growth and migration mainly through downregulation of MMP-2/9
protein expression. Therefore, the antitumour and anti-angiogenic efficacy of Fe-MIL-101 suggest that Fe-MIL-101 may be a promising novel candidate for cancer chemotherapy and our results
help provide new insights into the application of MOFs. METHODS CHEMICALS AND INSTRUMENTATION Terephthalic acid (H2BDC, 99%), ferric chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3•6H2O, 99%), ethanol (99.5%),
and _N, N_ dimethylformamide (DMF, 99.9%) were purchased from Alfa Aesar (Ward Hill, MA) and used for synthesis. All organic solvents were of analytical grade. Artesunate (C19H28O8, 98%, MW
= 384.4) was purchased from Guiling Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., (Guangxi, China). Oxaliplatin was purchased from Jiangsu Aosaikang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., (Nanjing, China). Doxorubicin
hydrochloride (8S,10S) -10-(4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yloxy) -,8,11 – trihydroxy -8- (2-hydroxyacetyl)-1-methoxy -7,8,9,10 -tetrahydrotetracene -5, 12-dione were
purchased from Alfa Aesar (Ward Hill, MA). The Annexin-V/PI detection apoptotic kit, JC1 lipophilic cation (5, 5′, 6, 6′ tetrachloro 1, 1′, 3, 3′ tetraethyl benzimidazol carbocyanine
iodide), and mitochondrial membrane potential detection kit were from Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology (Jiangsu, China). Fourier transform infrared measurements were performed on a
Nicolet 8700 instrument. X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) experiments were conducted on a D/max-3B spectrometer with Cu Kα radiation. Pore size distributions, BET surface areas and pore
volumes were measured by nitrogen adsorption/desorption measurements using a Micromeritics Tristar II Surface area and porosity analyser. Prior to the analysis, the samples were degassed at
90 °C for 1 h. Inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES) analysis was used to determine the contents of Fe3+ released from Fe-MIL-101. ICP-AES measurement was carried
out with a Shimadzu ICPS-1000IV model. Fluorescence spectroscopy measurements were carried out using a F-7000 FL Spectrophotometer. Cells were analysed using a FACSCalibur flow cytometer
(Becton Dickinson & Co., Franklin Lakes, NJ) and an Olympus IX73 microscope. SYNTHESIS OF FE-MIL-101 MOF Fe-MIL-101 was synthesized with ferric hydroxide and terephthalic acid according
to the literature1. Briefly, FeCl3•6H2O (0.675 g, 2.45 mmol) and H2BDC (0.206 g, 1.24 mmol) were added slowly into DMF (15 mL) solution. The mixture was stirred for 10 min at room
temperature, and then transferred into a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave and heated at 110 °C for 20 h. The resulting brown solid was filtered off, and the raw product was purified by
washing in hot ethanol (70 °C, 3 h), filtered off, and dried in an oven (70 °C, 30 min). The particles were isolated by centrifuging and washed with DMF and ethanol to remove any unreacted
starting materials. INCORPORATION OF ARTESUNATE AND DOXORUBICIN Artesunate (ART) and Doxorubicin (DOX) were loaded in Fe-MIL-101 according to the literature27. Briefly, 20 mg Fe-MIL-101 and
40 mg ART were added in 10 mL acetone solution and stirred for 72 hours. The precipitate was separated by centrifuging at 13 000 rpm and washed several times with acetone. Then, the
ART/Fe-MIL-101 was prepared and dried under vacuum during 3 days. The ART was quantified by was estimated by UV-Vis spectroscopy at 238 nm. The ART contents were determined to be 0.70 g of
ART per gram of the sample of Fe-MIL-101 (0.70 g/g material). 12.5 mg Fe-MIL-101 was added in 5 mL of a solution of DOX in ethanol (5 mg mL−1) under stirring at room temperature for 72
hours. The resulting nanoparticles were then purified by centrifugation and washed several times with ethanol. This process was repeated until no fluorescence signal from free,
non-encapsulated drug was detected in the supernatant solution. Then, the DOX/Fe-MIL-101 was prepared and dried under vacuum during 3 days. DOX was quantified by fluorescence spectroscopy
(emission maximum at 551 nm when excited at 472 nm). The DOX contents were determined to be 0.43 g of DOX per gram of the sample of Fe-MIL-101 (0.43 g/g material). CELL CULTURE BABL-3T3
mouse embryonic fibroblasts cells, A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells, HeLa human cervical cancer cells, and SKOV3 human ovarian cancer cells were purchased from the American Type Culture
Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA). The BABL-3T3 cell line was cultured in DMEM (high glucose) and other cells were grown in DMEM (low glucose) containing 10% fetal bovine serum. HUVECs
were isolated from term umbilical cord veins using collagenase and cultured in DMEM supplemented with 20% fetal bovine serum. All cell lines were grown at 37 °C in a humidified 5% CO2
atmosphere. HUVEC cells were used within 6 passages. MTT ASSAYS SKOV3, A549, HeLa, BABL-3T3 and HUVEC cells were plated in 96-well plates at a density of 1 × 104 cells per well. After 24 h
of culture in the normal growth medium, cells were exposed to various concentrations (1.56–25 μg mL−1) of Fe-MIL-101 for 24, 48 and 72 h. Cells were incubated with 5 μg mL−1 MTT solution for
4 h, and 150 μL DMSO was added for dissolving crystals. Absorbance at 490 nm was determined using a Spectra Max 190 microplate spectrophotometer (Molecular Devices Corporation, USA). Cell
numbers were obtained as absorbance values. The results were expressed as IC50 values. The experiment was repeated at least three times. CONDITIONED MEDIA SAMPLE PREPARATION AND THE EFFECT
OF FE-MIL-101 ON HUVEC PROLIFERATION IN CONDITIONED MEDIA Conditioned media (CM) was collected from P6 SKOV3 cells. Cells at 80–90% confluence were washed with PBS three times and incubated
with fresh DMEM without FBS medium (1 ml of medium per 9 cm2 of growth area) for 24 h at 37 °C. Media were then centrifuged (600 g, 10 min, 4 °C) and stored at −80 °C for further
experiments. Proliferation was assessed using the MTT assay in 96-well plates. HUVECs were incubated for 24 h in 10% FBS medium, and then replaced with 2% FBS media and incubated overnight
before treatment. VEGF (10 ng mL−1) and SU5416 (20 μM) were used as positive and negative control groups, respectively. Cells were exposed to of Fe-MIL-101 (25 μg mL−1). After 24 h, 5 μg
mL−1 MTT reagent was added in solution for 4 h, and 150 μL DMSO was added into plates for dissolving crystals. Absorbance at 490 nm was determined as described above. APOPTOSIS ASSAY BY
HOECHST 33342 STAINING HUVEC cells were seeded at a density of 2 × 105 cells/well on the surface of a cover slip in a 6-well plate in 2 mL medium containing 10% FBS. After 24 h, cells were
treated with Fe-MIL-101 (12.5 or 25 μg mL−1) and incubated for 48 h. Cells were washed with ice-cold PBS, and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min. The cells were incubated with Hoechst
33342 for 15 min at room temperature after washing three times with 2 mL of PBS. The cover slips were mounted on glass slides and the cells were analysed using a confocal fluorescence
microscopic system (Olympus IX73, Japan). FLOW CYTOMETRY ANALYSIS OF APOPTOTIC AND NECROTIC CELLS After chemical treatment, cells (1 × 106) were harvested, washed with PBS, fixed with 70%
ethanol, and maintained at 4 °C for at least 12 h. Pellets were stained with the fluorescent probe solution containing 5 μg mL−1 PI and 1 μg mL−1 FITC-Annexin-V in PBS on ice in dark for 15
min. The fluorescence emission was measured at 490 nm using 488-nm excitation by a FACSCalibur flow cytometer (Beckman Dickinson & Co., Franklin Lakes, NJ). A minimum of 1 × 104 cells
was analysed. MITOCHONDRIAL MEMBRANE POTENTIAL ASSAY HUVECs were treated with Fe-MIL-101 for 48 h in 24-well plates and washed three times with cold PBS. Cells were incubated with 5 μg mL−1
of JC1 for 20 min in culture medium at 37 °C in the dark. Cells were imaged under a fluorescence microscope (Olympus IX73, Japan). FLOW CYTOMETRY ANALYSIS OF CELL CYCLE HUVECs were seeded
into 6-well plates at a density of 1 × 106 cells per well and incubated for 24 h in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS at 37 °C and 5% CO2. The medium was removed and replaced with medium (final
DMSO concentration, 0.05% v/v) containing Fe-MIL-101 (3.12, 6.25, 12.5, or 25 μg mL−1). After incubation for 48 h, the cell layer was trypsinized, washed with PBS and fixed with 70%
ethanol. Next, 20 μL of RNAse (0.2 μg mL−1) and 20 μL of propidium iodide (0.02 μg mL−1) were added to the cell suspensions and they were incubated at 37 °C for 30 min. Samples were analysed
with a FACSCalibur flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson & Co., Franklin Lakes, NJ). A minimum of 1 × 104 cells was analysed. HUVEC MIGRATION ASSAY After cells were grown to confluence in a
6-well plate, cell monolayers were scratched with a 200-μL pipette tip. Cells were washed twice and the medium was replaced by fresh CM in DMEM. After 24 h under various conditions, the
number of migrated cells into the scratch area was quantified using an inverted microscope fitted with a digital camera (Olympus IX 73, Japan). TUBE FORMATION ASSAY Tubular network formation
assay was performed as described by Mirshahi64. Briefly, 50 μL Matrigel was added to each well of 96-well plates and the plates were incubated at 37 °C for 30 min for hardening. Then, 100
μL HUVEC suspensions (2 × 105 cells per mL), different doses of Fe-MIL-101, VEGF (10 ng mL−1) and CM were seeded on the Matrigel-coated plates for 12 h. In the other group, HUVECs
pre-treated with Fe-MIL-101 (12.5, 25 μg mL−1), VEGF (10 ng mL−1) and CM for 12 h were prepared by trypsinization, washed once with growth medium, and re-suspended at 2 × 105 cells per mL in
growth medium. Cells (100 μL) were gently added to the Matrigel-coated plates and incubated at 37 °C for 12 h. Tubular network formation was quantified by measuring the length of tubules in
randomly chosen five fields under a fluorescence microscope (Olympus IX73, Japan). The total length of a tube-like network in each photograph was measured using Adobe Photoshop TM software.
The inhibition percentage (%) of a sample was calculated by the following equation: inhibition percentage = (LC−LS) /LC × 100%, where LC is the average total capillary length of three
control wells and LS is the average total capillary length of the three sample-treated wells. WESTERN BLOT Cells were washed with cold PBS and resuspended in lysis buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl,
150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, SDS, 10% β-mercaptoethanol, 1 mM PMSF, EDTA and leupeptin) for 1 h on ice. The lysates were centrifuged at 4 °C for 15 min (14,000 g). Proteins were separated
by 10% SDS-PAGE and transferred onto PVDF membranes by standard procedures. Membranes were incubated sequentially with blocking agents (5% non-fat milk in PBS-Tween), primary antibodies
(MMP-2/9 1:200, β-actin 1:1000, GAPDH 1:3000) and HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies. The signal was detected by chemiluminescence agents. STATISTICAL ANALYSIS All values are expressed as
the mean ± S.D. and the significant levels between two groups were assessed by Student’s _t_-test. Results were considered statistically significant at 95% confidence interval (i.e., _P_
< 0.05). All figures and graphical readings shown were obtained from at least three independent experiments. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Wang, J. _et al_. Fe-MIL-101
exhibits selective cytotoxicity and inhibition of angiogenesis in ovarian cancer cells via downregulation of MMP. _Sci. Rep_. 6, 26126; doi: 10.1038/srep26126 (2016). REFERENCES * Ji, T.,
Zhao, Y., Ding, Y. & Nie, G. Using functional nanomaterials to target and regulate the tumor microenvironment: diagnostic and therapeutic applications. _Adv Mater._ 25, 3508–3525 (2013).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Weis, S. M. & Cheresh, D. A. Tumor angiogenesis: molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. _Nat. Med._ 17, 1359–1370 (2011). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Shibuya, M. Vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent and -independent regulation of angiogenesis. _BMB. Rep._ 4, 278–286 (2008). Article Google Scholar * Liu, Y. et al.
Delta-like ligand 4-targeted nanomedicine for antiangiogenic cancer therapy. _Biomaterials_ 42, 161–171 (2015). Article CAS Google Scholar * Song, H. et al. SiRNA directed against annexin
II receptor inhibits angiogenesis via suppressing MMP2 and MMP9 expression. _Cell Physiol. Biochem._ 35, 875–884 (2015). Article CAS Google Scholar * Nagababu, P. et al. Antiangiogenic
activity of mononuclear copper (II) polypyridyl complexes for the treatment of cancers. _J. Med. Chem._ 58, 5226–5241 (2015). Article CAS Google Scholar * Farinelle, S. et al.
Characterization of TNP-470-induced modifications to cell functions in HUVEC and cancer cells. _J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods._ 43, 15–24 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Mukherjee,
P. et al. Antiangiogenic properties of gold nanoparticles. _Clin. Cancer Res._ 11, 3530–3534 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Gurunathan, S. et al. Antiangiogenic properties of silver
nanoparticles. _Biomaterials_ 30, 6341–6350 (2009). Article CAS Google Scholar * Tang, Y., Jaganath, I. B., Manikam, R. & Sekaran, S. D. Phyllanthus spp. exerts anti-angiogenic and
anti- metastatic effects through inhibition on matrix metalloproteinase enzymes. _Nutr. Cancer_ 67, 783–795 (2015). Article Google Scholar * Kawasaki, E. S. & Player, A.
Nanotechnology, nanomedicine, and the development of new, effective therapies for cancer. _Nanomed- Nanotechnol._ 1, 101–109 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Ferrari, M. Cancer
nanotechnology: opportunities and challenges. _Nat. Rev. Cancer_ 5, 161–171 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Peynshaert, K. et al. Exploiting intrinsic nanoparticle toxicity: the pros
and cons of nanoparticle-induced autophagy in biomedical research. _Chem. Rev._ 114, 7581–7609 (2014). Article CAS Google Scholar * Arvizo, R. R. et al. Intrinsic therapeutic
applications of noble metal nanoparticles: past, present and future. _Chem. Soc. Rev._ 41, 2943–2970 (2012). Article CAS Google Scholar * Wei, L. et al. Silver nanoparticles: synthesis,
properties, and therapeutic applications. _Drug Discov. Today_ 20 595–601 (2015). Article CAS Google Scholar * Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J. et al. _In vivo_ behavior of large doses of ultrashort
and full-length single-walled carbon nanotubes after oral and intraperitoneal administration to swiss mice. _ACS Nano_ 4, 1481–1492 (2010). Article CAS Google Scholar * Wilhelm, C. &
Gazeau, F. Universal cell labelling with anionic magnetic nanoparticles. _Biomaterials_ 29, 3161–3174 (2008). Article CAS Google Scholar * Shakibaie, M. et al. Preparation and evaluation
of the effect of Fe3O4@piroctone olamine magnetic nanoparticles on matrix metalloproteinase-2: A preliminary _in vitro_ study. _Biotechnol. Appl. Bioc._ 61, 676–682 (2014). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Liu, Y. et al. Gd-metallofullerenol nanomaterial as non-toxic breast cancer stem cell-specific inhibitor. _Nat. Commun._ 6, 5988 (2015). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Pan, Y. et al. Gd-metallofullerenol nanomaterial suppresses pancreatic cancer metastasis by inhibiting the interaction of histone deacetylase 1 and metastasis-associated protein 1. _ACS
Nano_ 9, 6826–6836 (2015). Article CAS Google Scholar * Meng, H. et al. Potent angiogenesis inhibition by the particulate form of fullerene derivatives. _ACS Nano_ 4, 2773–2783 (2010).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Zuo, G., Kang, S. G., Xiu, P., Zhao, Y. & Zhou, R. Interactions between proteins and carbon-based nanoparticles: exploring the origin of nanotoxicity at
the molecular level. _Small_ 9, 1546–1556 (2013). Article CAS Google Scholar * Chen, Y. et al. Colloidal RBC-shaped, hydrophilic, and hollow mesoporous carbon nanocapsules for highly
efficient biomedical engineering. _Adv. Mater._ 26, 4294–4301 (2014). Article CAS Google Scholar * Purcell, B. P. et al. Injectable and bioresponsive hydrogels for on-demand matrix
metalloproteinase inhibition. _Nat. Mater._ 13, 653–661 (2014). Article CAS ADS Google Scholar * Skobelev, I. Y., Sorokin, A. B., Kovalenko, K. A., Fedin, V. P. & Kholdeeva, O. A.
Solvent-free allylic oxidation of alkenes with O2 mediated by Fe- and Cr-MIL-101. _J. Catal._ 298, 61–69 (2013). Article CAS Google Scholar * Falcaro, P. et al. A new method to position
and functionalize metal-organic framework crystals. _Nat. Commun._ 2, 237 (2011). Article Google Scholar * Horcajada, P. et al. Porous metal-organic-framework nanoscale carriers as a
potential platform for drug delivery and imaging. _Nat. Mater._ 9, 172–178 (2009). Article ADS Google Scholar * Huxford, R. C., DeKrafft, K. E., Boyle, W. S., Liu, D. & Lin, W.
Lipid-coated nanoscale coordination polymers for targeted delivery of antifolates to cancer cells. _Chem. Sci._ 3, 198–204 (2012). Article CAS Google Scholar * Wang, L., Li, L., Fan, Y.
& Wang, H. Host-guest supramolecular nanosystems for cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. _Adv. Mater._ 25, 3888–3898 (2013). Article CAS Google Scholar * Liu, D., Poon, C., Lu, K.,
He, C. & Lin, W. Self-assembled nanoscale coordination polymers with trigger release properties for effective anticancer therapy. _Nat. Commun._ 5, 4182 (2014). Article CAS ADS Google
Scholar * Férey, G. et al. A chromium terephthalate-based solid with unusually large pore volumes and surface area. _Science_ 309, 2040–2042 (2005). Article ADS Google Scholar * de
Lange, M. F., Verouden, K. J. F. M., Vlugt, T. J. H., Gascon, J. & Kapteijn, F., Adsorption-driven heat pumps: the potential of metal-organic frameworks. _Chem. Rev._ 115, 12205–12250,
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00059 (2015). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Chalati, T. et al. Porous metal organic framework nanoparticles to address the challenges related to busulfan
encapsulation. _Nanomedicine_ 6, 1683–1690 (2011). Article CAS Google Scholar * Tamames-Tabar, C. et al. Cytotoxicity of nanoscaled metal-organic frameworks. _J. Mater. Chem. B_ 2,
262–271 (2014). Article CAS Google Scholar * Baati, T. et al. In depth analysis of the _in vivo_ toxicity of nanoparticles of porous iron (III) metal-organic frameworks. _Chem. Science_
4, 1597–1607 (2013). Article CAS Google Scholar * Taylor-Pashow, K. M. L., Rocca, J. D., Xie, Z., Tran, S. & Lin, W. Postsynthetic modifications of iron-carboxylate nanoscale
metal-organic frameworks for imaging and drug delivery. _J. Am. Chem. Soc._ 131 14261–14263 (2009). Article CAS Google Scholar * Rieter, W. J., Pott, K. M., Taylor, K. M. L. & Lin, W.
Nanoscale coordination polymers for platinum-based anticancer drug delivery. _J. Am. Chem. Soc._ 130, 11584–11585 (2008). Article CAS Google Scholar * Ren, F. et al. Toxic effect of zinc
nanoscale metal-organic frameworks on rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells _in vitro_ . _J. Hazard. Mater._ 271, 283–291 (2014). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lucena, F. R. S. et al.
Induction of cancer cell death by apoptosis and slow release of 5-fluoracil from metal-organic frameworks Cu-BTC. _Biomed. Pharmacother._ 67, 707–713 (2013). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Wang, Y. et al. Cuprous oxide nanoparticles selectively induce apoptosis of tumor cells. _Int. J. Nanomed._ 7, 2641–2652 (2012). CAS Google Scholar * Huxford, R. C., Della Rocca, J. &
Lin, W. Metal–organic frameworks as potential drug carriers. _Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol._ 14, 262–268 (2010). Article CAS Google Scholar * Zhang, Z. et al. Synergy of 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin
D3 and carboplatin in growth suppression of SKOV3 cells. _Oncol. Lett._ 8, 1348–1354 (2014). Article CAS Google Scholar * Wang, L., Geng, M., Li, J., Guan, H. & Ding, J. Studies of
marine sulfated polymannuroguluronate on endothelial cell proliferation and endothelial immunity and related mechanisms. _J. Pharmacol Sci._ 92, 367–373 (2003). Article CAS Google Scholar
* Barui, A. K. et al. Zinc oxide nanoflowers make new blood vessels. _Nanoscale_ 4, 7861–7869 (2012). Article CAS ADS Google Scholar * Oh, S., Jeong, I. H., Shin, W. & Lee, S.
Growth inhibition activity of thioacetal artemisinin derivatives against human umbilical vein endothelial cells. _Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett._ 13, 3665–3668 (2003). Article CAS Google Scholar
* Gerber, H. P. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates endothelial cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/akt signal transduction pathway. _J. Biol. Chem._
273, 30336–30343 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Daoud, A., Song, J., Xiao, F. & Shang, J. B-9-3, a novel β-carboline derivative exhibits anti-cancer activity via induction of
apoptosis and inhibition of cell migration _in vitro_ . _Eur. J. Pharmacol._ 724, 219–230 (2014). Article CAS Google Scholar * Thress, K., Kornbluth, S. & Smith, J. J. Mitochondria at
the crossroad of apoptotic cell death. _J. Bioenerg. Biomembr._ 31, 321–326 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Sanpui, P., Chattopadhyay, A. & Ghosh, S. S. Induction of apoptosis
in cancer cells at low silver nanoparticle concentrations using chitosan nanocarrier. _ACS Appl. Mater. Inter._ 3, 218–228 (2011). Article CAS Google Scholar * Nuñez, M. T., Garate, M.
A., Arredondo, M., Tapia, V. & Muñoz, P. The cellular mechanisms of body iron homeostasis. _Biol. Res._ 33, 133–142 (2000). Article Google Scholar * Hentze, M. W., Muckenthaler, M. U.
& Andrews, N. C. Balancing acts: molecular control of mammalian iron metabolism. _Cell_ 117, 285–297 (2004). Article CAS Google Scholar * Mariappan, P., Krishnamoorthy, K.,
Kadarkaraithangam, J. & Govindasamy, M. Selective toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles toward gram-positive bacteria and cancer cells by apoptosis through lipid peroxidation. _Nanomedicine_ 7,
184–192 (2011). Article Google Scholar * AshaRani, P. V., Low, K. M. G., Hande, M. P. & Valiyaveettil, S. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. _ACS
Nano_ 3, 279–290 (2009). Article CAS Google Scholar * Meng, J., Liang, X., Chen, X. & Zhao, Y. Biological characterizations of [Gd@C82(OH)22]n nanoparticles as fullerene derivatives
for cancer therapy. _Integr. Biol._ 5, 43–47 (2013). Article CAS Google Scholar * Choudhury, D. et al. Unprecedented inhibition of tubulin polymerization directed by gold nanoparticles
inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. _Nanoscale_ 5, 4476–4489 (2013). Article CAS ADS Google Scholar * Nam, C., Kang, S., Kang, Y. K. & Kwak, M. Cell growth inhibition and
apoptosis by SDS-solubilized single-walled carbon nanotubes in normal rat kidney epithelial cells. _Arch. Pharm. Res._ 34, 661–669 (2011). Article CAS Google Scholar * Ye, Y., Liu, J.,
Chen, M., Sun, L. & Lan, M. _In vitro_ toxicity of silica nanoparticles in myocardial cells. _Environ. Toxicol. Phar._ 29, 131–137 (2010). Article CAS Google Scholar * Li, M. et al.
Arenobufagin, a bufadienolide compound from toad venom, inhibits VEGF-mediated angiogenesis through suppression of VEGFR-2 signalling pathway. _Biochem. Pharmacol._ 83, 1251–1260 (2012).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Winiarski, B. K. et al. Epithelial ovarian cancer-induced angiogenic phenotype of human omental microvascular endothelial cells may occur independently of
VEGF signalling. _Transl. Oncol._ 6, 703–714 (2013). Article Google Scholar * van der Bilt, A. R. et al. Multiple VEGF family members are simultaneously expressed in ovarian cancer: a
proposed model for bevacizumab resistance. _Curr. Pharm. Des._ 18, 3784–3792 (2012) Article CAS Google Scholar * Ghosh, S., Basu, M. & Roy, S. S., ETS-1 protein regulates vascular
endothelial growth factor-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 and matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in human oarian carcinoma cell line SKOV-3. _J. Biol. Chem._ 287, 15001–15015 (2012).
Article CAS Google Scholar * So, J., Wang, F., Navari, J., Schreher, J. & Fishman, D. A., LPA-induced epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) _in vitro_ invasion and migration are mediated by
VEGF receptor-2 (VEGF-R2). _Gynecol. Oncol._ 97, 870–878 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Wu, M. et al., Ultrasmall confined iron oxide nanoparticle MSNs as a pH-responsive
theranostic platform. _Adv. Funct. Mater._ 24, 4273–4283(2014). Article CAS Google Scholar * Mirshahi, P. et al. Vasculogenic mimicry of acute leukemic bone marrow stromal cells.
_Leukemia_ 23, 1039–1048 (2009). Article CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors thank National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project 21263027,
21573193, 21367024) and Program for Innovation Team of Yunnan Province and Innovative Research Team (in Science and Technology) in Universities of Yunnan Province and Key Laboratory of
Advanced Materials for Wastewater Treatment of Kunming for financial support. The authors also thank Key project from Yunnan Educational Committee (Project ZD2012003) for financial support.
AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Yunnan Provincial Collaborative Innovation Center of Green Chemistry for Lignite Energy, Yunnan Province Engineering Research Center of
Photocatalytic Treatment of Industrial Wastewater, The Universities’ Center for Photocatalytic Treatment of Pollutants in Yunnan Province, Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemistry for Natural
Resource, Ministry of Education, School of Energy, School of Chemical Sciences & Technology, Yunnan University, Kunming, 650091, P.R. China Jiaqiang Wang, Daomei Chen, Bin Li, Jiao He,
Deliang Duan, Dandan Shao & Minfang Nie Authors * Jiaqiang Wang View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Daomei Chen View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Bin Li View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Jiao He View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Deliang Duan View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Dandan Shao
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Minfang Nie View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
CONTRIBUTIONS J.W. and B.L. conceived the idea, supervised all aspects of this project and contributed to the paper. D.C. carried out the major part of experiments, analyzed the data and
contributed to the paper. J.H. and D.D. synthesized and characterized the MOF samples. M.N. carried out part of the cytotoxicity experiments. They and D.S. analyzed the data, were involved
in discussions, critical assessment, and manuscript improvements. CORRESPONDING AUTHORS Correspondence to Jiaqiang Wang or Bin Li. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare
no competing financial interests. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (DOC 594 KB) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0
International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the
material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Wang, J., Chen, D., Li, B. _et al._ Fe-MIL-101 exhibits selective cytotoxicity and
inhibition of angiogenesis in ovarian cancer cells via downregulation of MMP. _Sci Rep_ 6, 26126 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26126 Download citation * Received: 22 February 2016 *
Accepted: 22 April 2016 * Published: 18 May 2016 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26126 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get
shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative