Association between anthropometric indices and 5-year hypertension incidence in the general japanese population
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
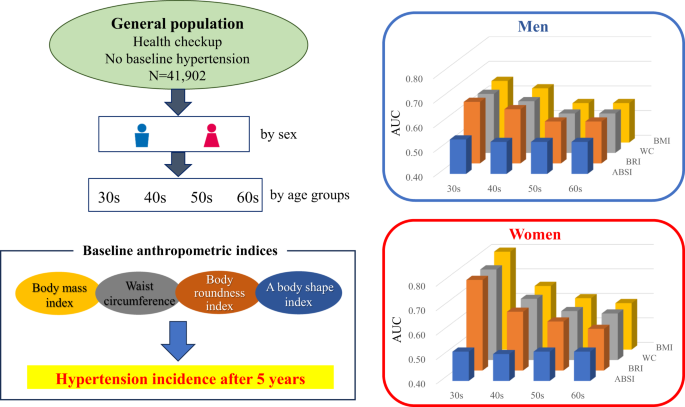
ABSTRACT No existing reports demonstrate the association between anthropometric indices (body mass index, waist circumference, body roundness index, a body shape index) and hypertension
according to sex and age in the general Japanese population. This retrospective analysis involved individuals aged 30–69 years who underwent annual medical checkups at Kagoshima Koseiren
Hospital in 2005–2019, and who did not meet hypertension criteria at baseline. The outcome was hypertension incidence after 5 years, and its association with baseline anthropometric indices
was evaluated using multivariable logistic regression analysis by sex and age. In 41,902 participants (age 52.3 ± 10.2 years, 47.7% men), 7622 individuals (18.2%) developed hypertension
after 5 years. Body mass index, waist circumference, and body roundness index were significantly associated with the development of hypertension in both men and women across all age
categories from 30 s to 60 s. In the population with a body mass index <25 kg/m2, waist circumference and body roundness index were significantly associated with hypertension after 5
years. A body shape index was significantly associated with the development of hypertension in men in their 40 s and 50 s but not in women of any age group. The area under the curve values
were lower for a body shape index than for body mass index, waist circumference, and body roundness index in both men and women of all age groups. A body shape index was not a stronger
indicator for 5-year hypertension incidence than body mass index, waist circumference, or body roundness index in both men and women across age groups from their 30s–60 s. The results of
this study will help to more efficiently identify populations at high risk of developing hypertension and provide preventive interventions. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are
calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS
COMPARISON OF CONVENTIONAL AND UNCONVENTIONAL OBESITY INDICES ASSOCIATED WITH NEW-ONSET HYPERTENSION IN DIFFERENT SEX AND AGE POPULATIONS Article Open access 13 May 2023 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
OF ADIPOSITY INDICES FOR PREDICTING 2-YEAR HYPERTENSION INCIDENCE IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS: A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Article Open access 10 June 2025 PREVALENCE OF OBESITY AND AN
INTERROGATION OF THE CORRELATION BETWEEN ANTHROPOMETRIC INDICES AND BLOOD PRESSURES IN URBAN LAGOS, NIGERIA Article Open access 10 February 2021 DATA AVAILABILITY The deidentified data of
participants will not be shared. REFERENCES * Mills KT, Bundy JD, Kelly TN, Reed JE, Kearney PM, Reynolds K, et al. Global disparities of hypertension prevalence and control: a systematic
analysis of population-based studies from 90 countries. Circulation. 2016;134:441–50. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * GBD 2019 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden of
87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2020;396:1223–49. Article Google Scholar * Ikeda N,
Inoue M, Iso H, Ikeda S, Satoh T, Noda M, et al. Adult mortality attributable to preventable risk factors for non-communicable diseases and injuries in Japan: a comparative risk assessment.
PLOS Med. 2012;9:e1001160. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Nakamura K, Okamura T, Kanda H, Hayakawa T, Kadowaki T, Okayama A, et al. Impact of hypertension on medical
economics: a 10-year follow-up study of national health insurance in Shiga, Japan. Hypertens Res. 2005;28:859–64. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Patel P, Ordunez P, DiPette D, Escobar
MC, Hassell T, Wyss F, et al. Improved blood pressure control to reduce cardiovascular disease morbidity and mortality: the standardized hypertension treatment and prevention project. Rev
Panam Salud Publica. 2017;41:1. PubMed Google Scholar * Vooradi S, Mateti UV. A systemic review on lifestyle interventions to reduce blood pressure. J Health Res Rev. 2016;3:1–5. Article
Google Scholar * Krauss RM, Winston M, Fletcher BJ, Grundy SM. Obesity: impact on cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 1998;98:1472–6. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Rao G, Powell-Wiley
TM, Ancheta I, Hairston K, Kirley K, Lear SA, et al. Identification of obesity and cardiovascular risk in ethnically and racially diverse populations: a scientific statement from the
American Heart Association. Circulation. 2015;132:457–72. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Krakauer NY, Krakauer JC. A new body shape index predicts mortality hazard independently of body
mass index. PLOS ONE. 2012;7:e39504. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Thomas DM, Bredlau C, Bosy-Westphal A, Mueller M, Shen W, Gallagher D, et al. Relationships
between body roundness with body fat and visceral adipose tissue emerging from a new geometrical model. Obes (Silver Spring). 2013;21:2264–71. Article Google Scholar * Xu J, Zhang L, Wu Q,
Zhou Y, Jin Z, Li Z, et al. Body roundness index is a superior indicator to associate with the cardio‐metabolic risk: evidence from a cross‐sectional study with 17,000 Eastern-China adults.
BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021;21:97. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Kawasoe M, Kawasoe S, Kubozono T, Ojima S, Kawabata T, Ikeda Y, et al. Development of a risk prediction
score for hypertension incidence using Japanese health checkup data. Hypertens Res. 2022;45:730–40. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Matsuzawa Y, Definition and the diagnostic standard
for metabolic syndrome–Committee to Evaluate Diagnostic Standards for Metabolic Syndrome. Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi. 2005; 94: 794–809. * Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E,
Azizi M, Burnier M, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of
Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of
Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2018;36:1953–2041. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hall JE, do Carmo JM, da Silva AA, Wang Z, Hall ME. Obesity-induced hypertension: interaction of
neurohumoral and renal mechanisms. Circ Res. 2015;116:991–1006. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Appel LJ, Brands MW, Daniels SR, Karanja N, Elmer PJ, Sacks FM, et al.
Dietary approaches to prevent and treat hypertension: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension. 2006;47:296–308. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Neter JE, Stam BE, Kok FJ, Grobbee DE, Geleijnse JM. Influence of weight reduction on blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hypertension. 2003;42:878–84. Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Channanath AM, Farran B, Behbehani K, Thanaraj TA. Association between body mass index and onset of hypertension in men and women with and without diabetes: a
cross-sectional study using national health data from the State of Kuwait in the Arabian Peninsula. BMJ Open. 2015;5:e007043. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Nevill AM,
Stewart AD, Olds T, Holder R. Relationship between adiposity and body size reveals limitations of BMI. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2006;129:151–6. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Li C, Ford ES,
McGuire LC, Mokdad AH. Increasing trends in waist circumference and abdominal obesity among US adults. Obes (Silver Spring). 2007;15:216–24. Article Google Scholar * Bosomworth NJ.
Normal-weight central obesity: unique hazard of the toxic waist. Can Fam Physician. 2019;65:399–408. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Camhi SM, Bray GA, Bouchard C, Greenway FL,
Johnson WD, Newton RL, et al. The relationship of waist circumference and BMI to visceral, subcutaneous, and total body fat: sex and race differences. Obes (Silver Spring). 2011;19:402–8.
Article Google Scholar * Cheng C, Sun JY, Zhou Y, Xie QY, Wang LY, Kong XQ, et al. High waist circumference is a risk factor for hypertension in normal-weight or overweight individuals
with normal metabolic profiles. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2022;24:908–17. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ashwell M, Gunn P, Gibson S. Waist-to-height ratio is a better screening
tool than waist circumference and BMI for adult cardiometabolic risk factors: systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2012;13:275–86. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Deng G,
Yin L, Liu W, Liu X, Xiang Q, Qian Z, et al. Associations of anthropometric adiposity indexes with hypertension risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis including PURE-China. Medicine.
2018;97:e13262. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chang Y, Guo X, Guo L, Li Z, Li Y, Sun Y. The feasibility of two new anthropometric indices to identify hypertension in
rural China: a cross-sectional study. Med (Balt). 2016;95:e5301. Article Google Scholar * Ji M, Zhang S, An R. Effectiveness of a body shape index (ABSI) in predicting chronic diseases and
mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2018;19:737–59. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Fujita M, Sato Y, Nagashima K, Takahashi S, Hata A. Predictive power of a
body shape index for development of diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia in Japanese adults: a retrospective cohort study. PLOS ONE. 2015;10:e0128972. Article PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Silva AM, Shen W, Heo M, Gallagher D, Wang Z, Sardinha LB, et al. Ethnicity-related skeletal muscle differences across the lifespan. Am J Hum Biol. 2010;22:76–82. Article
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Lear SA, Humphries KH, Kohli S, Chockalingam A, Frohlich JJ, Birmingham CL. Visceral adipose tissue accumulation differs according to ethnic
background: results of the Multicultural Community Health Assessment Trial (M-CHAT). Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:353–9. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Tsou MT, Chang YC, Hsu CP, Kuo YC,
Yun CH, Huang WH, et al. Visceral adiposity index outperforms conventional anthropometric assessments as predictor of diabetes mellitus in elderly Chinese: a population-based study. Nutr
Metab (Lond). 2021;18:87. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Cheung YB. “A Body Shape Index” in middle-age and older Indonesian population: scaling exponents and association
with incident hypertension. PLoS One. 2014;9:e85421. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Wilmet G, Verlinde R, Vandevoorde J, Carnol L, Devroey D. Correlation between body
mass index and abdominal circumference in Belgian adults: a cross-sectional study. Rom J Intern Med. 2017;55:28–35. PubMed Google Scholar * Maessen MF, Eijsvogels TM, Verheggen RJ, Hopman
MT, Verbeek AL, de Vegt F. Entering a new era of body indices: the feasibility of a body shape index and body roundness index to identify cardiovascular health status. PLOS ONE.
2014;9:e107212. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Kajikawa M, Maruhashi T, Kishimoto S, Yamaji T, Harada T, Hashimoto Y, et al. A body shape index is associated with
endothelial dysfunction in both men and women. Sci Rep. 2021;11:17873. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Zhang Y, Yang H, Ren M, Wang R, Zhao F, Liu T, et al.
Distribution of risk factors of hypertension patients in different age groups in Tianjin. BMC Public Health. 2021;21:247. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Download references
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank the medical staff at Kagoshima Kouseiren Hospital for their support in data collection. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Cardiovascular
Medicine and Hypertension, Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences, Kagoshima University, Kagoshima, Japan Shin Kawasoe, Takuro Kubozono, Anwar Ahmed Salim, Satoko Ojima, Satoshi
Yamaguchi, Yoshiyuki Ikeda & Mitsuru Ohishi * Kagoshima Kouseiren Hospital, Kagoshima, Japan Hironori Miyahara & Koichi Tokushige * School of Health Sciences, Faculty of Medicine,
Kagoshima University, Kagoshima, Japan Masaaki Miyata Authors * Shin Kawasoe View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Takuro Kubozono View
author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Anwar Ahmed Salim View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar *
Satoko Ojima View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Satoshi Yamaguchi View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar * Yoshiyuki Ikeda View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Hironori Miyahara View author publications You can also search for
this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Koichi Tokushige View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Masaaki Miyata View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Mitsuru Ohishi View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence
to Takuro Kubozono. ETHICS DECLARATIONS CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare no competing interests. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION PUBLISHER’S NOTE Springer Nature remains neutral with regard
to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY TABLE 1 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLE 2 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLE 3 RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author
self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law. Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE
CITE THIS ARTICLE Kawasoe, S., Kubozono, T., Salim, A.A. _et al._ Association between anthropometric indices and 5-year hypertension incidence in the general Japanese population. _Hypertens
Res_ 47, 867–876 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-023-01505-6 Download citation * Received: 14 August 2023 * Revised: 17 October 2023 * Accepted: 20 October 2023 * Published: 15
November 2023 * Issue Date: April 2024 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-023-01505-6 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get
shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS *
Hypertension * Obesity * Body roundness index * A body shape index