Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation is equally effective in secondary acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) compared to de-novo ALL—a report from the EBMT registry
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
Secondary acute lymphoblastic leukemia (s-ALL) comprises up to 10% of ALL patients. However, data regarding s-ALL outcomes is limited. To answer what is the role of allogeneic hematopoietic
cell transplantation (HCT) in s-ALL, a matched-pair analysis in a 1:2 ratio was conducted to compare outcomes between s-ALL and de novo ALL (dn-ALL) patients reported between 2000–2021 to
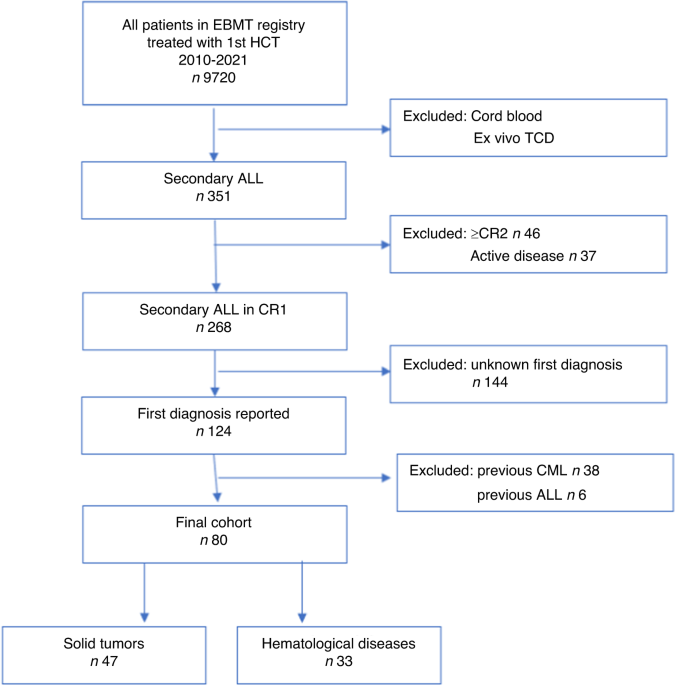
the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation registry. Among 9720 ALL patients, 351 (3.6%) were s-ALL, of which 80 were in first complete remission (CR1) with a known precedent
primary diagnosis 58.8% solid tumor (ST), 41.2% hematological diseases (HD). The estimated 2-year relapse incidence (RI) was 19.1% (95%CI: 11–28.9), leukemia-free survival (LFS) 52.1%
(95%CI: 39.6–63.2), non-relapse mortality (NRM) 28.8% (95%CI: 18.4–40), GvHD-free, relapse-free survival (GRFS) 39.4% (95%CI: 27.8–50.7), and overall survival (OS) 60.8% (95%CI: 47.9–71.4),
and did not differ between ST and HD patients. In a matched-pair analysis, there was no difference in RI, GRFS, NRM, LFS, or OS between s-ALL and dn-ALL except for a higher incidence of
chronic GvHD (51.9% vs. 31.4%) in s-ALL. To conclude, patients with s-ALL who received HCT in CR1 have comparable outcomes to patients with dn-ALL.
ASK, JMZ, ML, and MM had full access to all study data (available upon data-specific request).
ASK wrote the manuscript, designed the study, and interpreted the data. JMZ and MM designed the study, interpreted the data, and edited the manuscript. ML designed the study, performed the
statistical analyses, interpreted the data, and edited the manuscript. JHB, DB, IYA, US, JP, NF, TS, SG, EB, and FC reviewed the manuscript and provided clinical data. All authors approved
the final version of the manuscript.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author
self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: