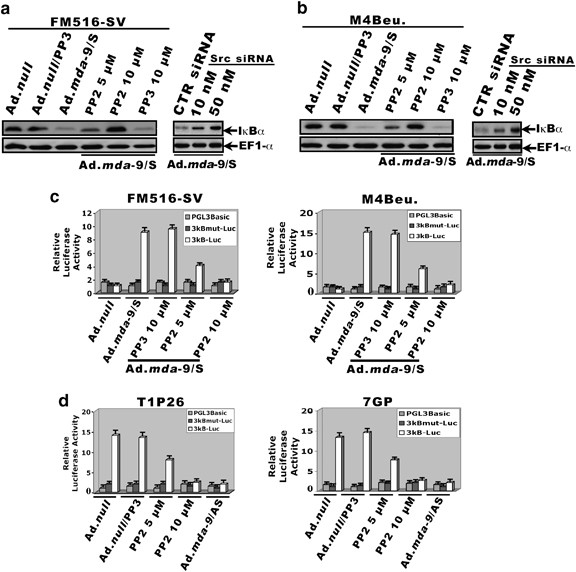
Src kinase activation is mandatory for mda-9/syntenin-mediated activation of nuclear factor-κb
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT The scaffolding postsynaptic density-95/disks large/zonula occludens-1 (PDZ) domain-containing protein melanoma differentiation associated gene-9 (MDA-9)/syntenin is a tandem PDZ
protein overexpressed in human melanoma, and breast and gastric cancer cells. MDA-9/syntenin affects cancer cell motility and invasion through distinct biochemical and signaling pathways,
including focal adhesion kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), resulting in activation of the nuclear factor (NF)-κB pathway. MDA-9/syntenin also promotes melanoma
metastasis by activating c-_Src_, but how c-_Src_ regulates NF-κB activation is unclear. Using a human melanoma model, we document that MDA-9/syntenin–c-Src interactions are positive
regulators of NF-κB activation. Inhibition of _c-Src_ by PP2 treatment, by blocking c-_Src_ or _mda-_9/syntenin expression with small interfering RNA, or in c-_Src_ (−/−) knockout cell
lines, reduces NF-κB activation following overexpression of _mda-_9/syntenin or _c-Src_. Deletion or point mutations of the PDZ binding motif preventing MDA-9/syntenin association with c-Src
reveals that both PDZ domains, with PDZ2 being the dominant module, are required for activating downstream signaling pathways, including p38 MAPK and NF-κB. We also document that
MDA-9/syntenin–c-Src complexes functionally cooperate with NF-κB to promote anchorage-independent growth, motility and invasion of melanoma cells. These findings underscore PDZ domains of
MDA-9/syntenin as promising potential therapeutic targets for intervening in a decisive component of cancer progression, namely, metastatic tumor spread. Access through your institution Buy
or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 50 print issues and
online access $259.00 per year only $5.18 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes
which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY
OTHERS MDM2 REQUIRES SPROUTY4 TO REGULATE FOCAL ADHESION FORMATION AND METASTASIS INDEPENDENT OF P53 Article Open access 20 August 2024 INTERACTION OF LATS1 WITH SMAC LINKS THE MST2/HIPPO
PATHWAY WITH APOPTOSIS IN AN IAP-DEPENDENT MANNER Article Open access 08 August 2022 PHOSPHORYLATION OF THE PROLINE-RICH DOMAIN OF WAVE3 DRIVES ITS ONCOGENIC ACTIVITY IN BREAST CANCER
Article Open access 16 February 2021 REFERENCES * Aikawa R, Komuro I, Yamazaki T, Zou Y, Kudoh S, Tanaka M _et al_. (1997). Oxidative stress activates extracellular signal-regulated kinases
through Src and Ras in cultured cardiac myocytes of neonatal rats. _J Clin Invest_ 100: 1813–1821. Article CAS Google Scholar * Baril P, Nejjari M, Scoazek JY, Boukerche H . (2002).
Blocking a novel 55 kDa melanoma-associated cell surface antigen inhibits the development of spontaneous metastases and interactions with frozen lung section. _Int J Cancer_ 99: 315–322.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Bass MD, Humphries MJ . (2002). Cytoplasmic interactions of syndecan-4 orchestrate adhesion receptor and growth factor receptor signalling. _Biochem J_ 368:
1–15. Article CAS Google Scholar * Boukerche H, Baril P, Tabone E, Bérard F, Sanhadji K, Balme B _et al_. (2000). A new Mr 55 000 surface protein implicated in melanoma progression:
association with a metastatic phenotype. _Cancer Res_ 60: 5848–5856. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Boukerche H, Su ZZ, Kang DC, Fisher PB . (2004). Identification and cloning of genes
displaying elevated expression as a consequence of metastatic progression in human melanoma cells by rapid subtraction hybridization. _Gene_ 343: 191–201. Article CAS Google Scholar *
Boukerche H, Su ZZ, Emdad L, Baril P, Balme B, Thomas L _et al_. (2005). mda 9/Syntenin: a positive regulator of melanoma metastasis. _Cancer Res_ 65: 10901–10911. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Boukerche H, Su ZZ, Emdad L, Sarkar D, Fisher PB . (2007). mda-9/Syntenin regulates the metastatic phenotype in human melanoma cells by activating nuclear factor-kappaB. _Cancer
Res_ 67: 1812–1822. Article CAS Google Scholar * Boukerche H, Su ZZ, Prévot C, Sarkar D, Fisher PB . (2008). mda-9/Syntenin promotes metastasis in human melanoma cells by activating
c-Src. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 105: 15914–15919. Article CAS Google Scholar * Chen K, Vita JA, Berk BC, Keaney Jr JF . (2001). c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation by hydrogen peroxide in
endothelial cells involves SRC-dependent epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation. _J Biol Chem_ 276: 16045–16050. Article CAS Google Scholar * Chu QS, Forouzesh B, Syed S, Mita
M, Schwartz G, Cooper J . (2007). A phase II and pharmacological study of the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor (MMPI) COL-3 in patients with advanced soft tissue sarcomas. _Invest New
Drugs_ 25: 359–367. Article CAS Google Scholar * Dong H, O'Brien RJ, Fung ET, Lanahan AA, Worley PF, Huganir RL . (1997). GRIP: a synaptic PDZ domain-containing protein that
interacts with AMPA receptors. _Nature_ 386: 279–284. Article CAS Google Scholar * Fidler IJ, Li LM, Ananthaswamy HN, Esumi N, Radinsky R, Price JE . (1991). Correlation of growth
capacity of cells in hard agarose with successful transfection by the activated c-Ha-ras oncogene and _in vivo_ proliferative capacity at metastatic sites. _Anticancer Res_ 11: 17–24. CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Funakoshi-Tago M, Tago K, Andoh K, Sonoda Y, Tominaga S, Kasahara T . (2005). Functional role of c-Src in IL-1-induced NF-kappa B activation: c-Src is a component
of the IKK complex. _J Biochem_ 137: 189–197. Article CAS Google Scholar * Galliher-Beckley AJ, Schiemann WP . (2008). Grb2 binding to Tyr284 in TbetaR-II is essential for mammary tumor
growth and metastasis stimulated by TGF-beta. _Carcinogenesis_ 29: 244–251. Article CAS Google Scholar * Geijsen N, Uings IJ, Pals C, Armstrong J, McKinnon M, Raaijmakers JA _et al_.
(2001). Cytokine-specific transcriptional regulation through an IL-5Ralpha interacting protein. _Science_ 293: 1136–1138. Article CAS Google Scholar * Grootjans JJ, Reekmans G, Ceulemans
H, David G . (2000). Syntenin-syndecan binding requires syndecan-synteny and the co-operation of both PDZ domains of syntenin. _J Biol Chem_ 275: 19933–19941. Article CAS Google Scholar *
Hanke JH, Gardner JP, Dow RL, Changelian PS, Brissette WH, Weringer EJ _et al_. (1996). Discovery of a novel, potent, and Src family-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Study of Lck- and
FynT-dependent T cell activation. _J Biol Chem_ 271: 695–701. Article CAS Google Scholar * Helmke BM, Polychronidis M, Benner A, Thome M, Arribas J, Deichmann M . (2004). Melanoma
metastasis is associated with enhanced expression of the syntenin gene. _Oncol Rep_ 12: 221–228. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hofmann WA, Stojiljkovic L, Fuchsova B, Vargas GM, Mavrommatis
E, Philimonenko V _et al_. (2004). Actin is part of pre-initiation complexes and is necessary for transcription by RNA polymerase II. _Nat Cell Biol_ 6: 1094–1101. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Hirbec H, Martin S, Henley JM . (2005). Syntenin is involved in the developmental regulation of neuronal membrane architecture. _Mol Cell Neurosci_ 28: 737–746. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Jalali S, Li YS, Sotoudeh M, Yuan S, Li S, Chien S _et al_. (1998). Shear stress activates p60src-Ras-MAPK signaling pathways in vascular endothelial cells. _Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol_ 18: 227–234. Article CAS Google Scholar * Jannatipour M, Dion P, Khan S, Jindal H, Fan X, Laganière J _et al_. (2001). Schwannomin isoform-1 interacts with syntenin via
PDZ domains. _J Biol Chem_ 276: 33093–33100. Article CAS Google Scholar * Kang BS, Cooper DR, Jelen F, Devedjiev Y, Derewenda U, Dauter Z _et al_. (2003). PDZ tandem of human syntenin:
crystal structure and functional properties. _Structure_ 11: 459–468. Article CAS Google Scholar * Klinghoffer RA, Sachsenmaier C, Cooper JA, Soriano P . (1999). Src family kinases are
required for integrin but not PDGFR signal transduction. _EMBO J_ 18: 2459–2471. Article CAS Google Scholar * Koo TH, Lee JJ, Kim EM, Kim KW, Kim HD, Lee JH . (2002). Syntenin is
overexpressed and promotes cell migration in metastatic human breast and gastric cancer cell lines. _Oncogene_ 21: 4080–4088. Article CAS Google Scholar * Koroll M, Rathjen FG, Volkmer H
. (2001). The neural cell recognition molecule neurofascin interacts with syntenin-1 but not with syntenin-2, both of which reveal self-associating activity. _J Biol Chem_ 276: 10646–10654.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Lee HS, Moon C, Lee HW, Park EM, Cho MS, Kang JL . (2007). Src tyrosine kinases mediate activations of NF-kappaB and integrin signal during
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. _J Immunol_ 179: 7001–7011. Article CAS Google Scholar * Lin JJ, Jiang H, Fisher PB . (1996). Characterization of a novel melanoma
differentiation-associated gene, mda-9, that is down regulated during terminal differentiation. _Mol Cell Differ_ 4: 317–333. Google Scholar * Lin JJ, Jiang H, Fisher PB . (1998). Melanoma
differentiation associated gene-9, mda-9, is a human gamma interferon responsive gene. _Gene_ 207: 105–110. Article CAS Google Scholar * Liu AM, Wong YH . (2005). Activation of nuclear
factor {kappa}B by somatostatin type 2 receptor in pancreatic acinar AR42J cells involves G{alpha}14 and multiple signaling components: a mechanism requiring protein kinase C,
calmodulin-dependent kinase II, ERK, and c-Src. _J Biol Chem_ 280: 34617–34625. Article CAS Google Scholar * Matsuo Y, Amano S, Furuya M, Namiki K, Sakurai K, Nishiyama M _et al_. (2006).
Involvement of p38alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase in lung metastasis of tumor cells. _J Biol Chem_ 281: 36767–36775. Article CAS Google Scholar * Meerschaert K, Bruyneel E, De
Wever O, Vanloo B, Boucherie C, Bracke M _et al_. (2007). The tandem PDZ domains of syntenin promote cell invasion. _Exp Cell Res_ 313: 1790–1804. Article CAS Google Scholar * Mikami F,
Gu H, Jono H, Andalibi A, Kai H, Li JD . (2005). Epidermal growth factor receptor acts as a negative regulator for bacterium nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae-induced Toll-like receptor 2
expression via an Src-dependent p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. _J Biol Chem_ 280: 36185–36194. Article CAS Google Scholar * Orlowski RZ, Baldwin Jr AS . (2002).
NF-kappaB as a therapeutic target in cancer. _Trends Mol Med_ 8: 385–389. Article CAS Google Scholar * Perez DG, Suman VJ, Fitch TR, Amatruda 3rd T, Morton RF, Jilani SZ _et al_. (2009).
Phase 2 trial of carboplatin, weekly paclitaxel, and biweekly bevacizumab in patients with unresectable stage IV melanoma: a North Central Cancer Treatment Group study, N047A. _Cancer_ 115:
119–127. Article CAS Google Scholar * Petro JB, Rahma SM, Ballard DW, Khan WN . (2000). Bruton's tyrosine kinase is required for activation of IkappaB kinase and nuclear factor
kappaB in response to B cell receptor engagement. _J Exp Med_ 19: 1745–1754. Article Google Scholar * Ponting CP, Phillips C, Davies KE, Blake DJ . (1997). PDZ domains: targeting
signalling molecules to sub-membranous sites. _Bioessays_ 19: 469–479. Article CAS Google Scholar * Posern G, Sotiropoulos A, Treisman R . (2002). Mutant actins demonstrate a role for
unpolymerized actin in control of transcription by serum response factor. _Mol Biol Cell_ 13: 4167–4178. Article CAS Google Scholar * Rivas FV, O'Keefe JP, Alegre ML, Gajewski TF .
(2004). Actin cytoskeleton regulates calcium dynamics and NFAT nuclear duration. _Mol Cell Biol_ 24: 1628–1639. Article CAS Google Scholar * Sarkar D, Boukerche H, Su ZZ, Fisher PB .
(2008). mda-9/syntenin: more than just a simple adapter protein when it comes to cancer metastasis. _Cancer Res_ 68: 3087–3093. Article CAS Google Scholar * Sarkar D, Boukerche H, Su ZZ,
Fisher PB . (2004). mda-9/syntenin: recent insights into a novel cell signaling and metastasis-associated gene. _Pharmacol Ther_ 104: 101–115. Article CAS Google Scholar * Sarkar FH, Li
Y, Wang Z, Kong D . (2008). NF-kappaB signaling pathway and its therapeutic implications in human diseases. _Int Rev Immunol_ 27: 293–319. Article CAS Google Scholar * Schultz J, Copley R
R, Doerks T, Ponting CP, Bork P . (2000). SMART: a web-based tool for the study of genetically mobile domains. _Nucleic Acids Res_ 28: 231–234. Article CAS Google Scholar * Storz P,
Toker A . (2003). Protein kinase D mediates a stress-induced NF-kappaB activation and survival pathway. _EMBO J_ 22: 109–120. Article CAS Google Scholar * Sulka B, Lortat-Jacob H, Terreux
R, Letourneur F, Rousselle P . (2009). Tyrosine dephosphorylation of the syndecan-1 PDZ binding domain regulates syntenin-1 recruitment. _J Biol Chem_ 284: 10659–10671. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Ten RM, McKinstry MJ, Trushin SA, Asin S, Paya CV . (1999). The signal transduction pathway of CD23 (Fc epsilon RIIb) targets I kappa B kinase. _J Immunol_ 163: 3851–3857. CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Volonte D, Galbiati F, Pestell RG, Lisanti MP . (2001). Cellular stress induces the tyrosine phosphorylation of caveolin-1 (Tyr(14)) via activation of p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Src kinase: evidence for caveolae, the actin cytoskeleton, and focal adhesions as mechanical sensors of osmotic stress. _J Biol Chem_ 276: 8094–8103.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Warmuth M, Damoiseaux R, Liu Y, Fabbro D, Gray N . (2003). SRC family kinases: potential targets for the treatment of human cancer and leukemia. _Curr Pharm
Des_ 9: 2043–2059. Article CAS Google Scholar * Zhang Q, Fan JS, Zhan M . (2001). Interdomain chaperoning between PSD-95, Dlg, and ZO-1 (PDZ) domains of glutamate receptor-interacting
proteins. _J Biol Chem_ 276: 43216–43220. Article CAS Google Scholar * Zhou J, Menko AS . (2004). Coordinate signaling by Src and p38 kinases in the induction of cortical cataracts.
_Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci_ 45: 2314–2323. Article Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health, National Cancer
Institute Grants R01 CA035675 and CA097318, the Samuel Waxman Cancer Research Foundation (SWCRF), the National Foundation for Cancer Research (NFCR) (PBF); the Goldhirsh Foundation and the
Dana Foundation (DS); and the Ligue nationale contre le Cancer and Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer grant 1019 (HB). DS is the Harrison Endowed Scholar in Cancer Research and PBF
holds the Thelma Newmeyer Corman Chair in Cancer Research at the VCU Massey Cancer Center. PBF is a SWCRF Investigator. AUTHOR INFORMATION Author notes * H Boukerche and H Aissaoui: These
authors contributed equally to this work. AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Human and Molecular Genetics, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA, USA H Boukerche, S K Das, Z-Z
Su, D Sarkar & P B Fisher * EA4174, Université Claude Bernard, Lyon 1 INSERM, Lyon, France H Boukerche, H Aissaoui & C Prévost * INSERM U583, Montpellier, France H Hirbec * VCU
Massey Cancer Center, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA, USA D Sarkar & P B Fisher * VCU Institute of Molecular Medicine, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA, USA
D Sarkar & P B Fisher Authors * H Boukerche View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * H Aissaoui View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * C Prévost View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * H Hirbec View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * S K Das View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Z-Z Su View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * D Sarkar View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * P B Fisher View author publications You
can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHORS Correspondence to H Boukerche or P B Fisher. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no
conflict of interest. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Boukerche, H., Aissaoui, H., Prévost, C. _et al._ Src kinase activation is
mandatory for MDA-9/syntenin-mediated activation of nuclear factor-κB. _Oncogene_ 29, 3054–3066 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.65 Download citation * Received: 20 November 2009 *
Revised: 21 January 2010 * Accepted: 29 January 2010 * Published: 15 March 2010 * Issue Date: 27 May 2010 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.65 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the
following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer
Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * mda-9/syntenin * src * NF-κB