RNA-binding protein HuR mediates cytoprotection through stimulation of XIAP translation
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
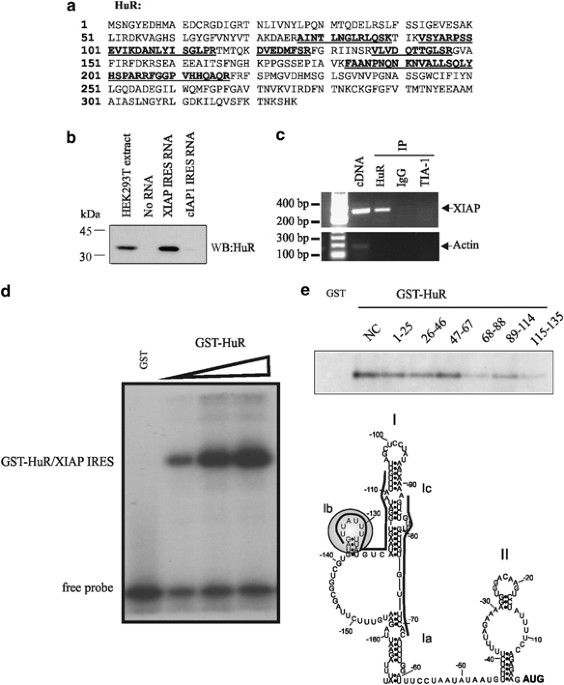
Expression of the intrinsic cellular caspase inhibitor XIAP is regulated primarily at the level of protein synthesis. The 5′ untranslated region harbours an Internal Ribosome Entry Site
(IRES) motif that supports cap-independent translation of XIAP mRNA during conditions of cellular stress. In this study, we show that the RNA-binding protein HuR, which is known to
orchestrate an antiapoptotic cellular program, stimulates translation of XIAP mRNA through XIAP IRES. We further show that HuR binds to XIAP IRES in vitro and in vivo, and stimulates
recruitment of the XIAP mRNA into polysomes. Importantly, protection from the apoptosis-inducing agent etoposide by overexpression of HuR requires the presence of XIAP, suggesting that
HuR-mediated cytoprotection is partially executed through enhanced XIAP translation. Our data suggest that XIAP belongs to the HuR-regulated RNA operon of antiapoptotic genes, which, along
with Bcl-2, Mcl-1 and ProTα, contributes to the regulation of cell survival.
We thank Drs Nehal Thakor and Stephen Baird for critical discussions. We are grateful to Drs P Anderson and R Screaton for the gift of anti-TIA-1/TIAR and anti-GST antibodies, respectively,
and to Dr I Gallouzi for the GFP-HuR, GFP-HuR(CP1), GFP-HuR(CP2), AP-HuR-GST, AP-HuR(CP1)-GST and AP-HuR(CP2)-GST overexpression constructs. This work was supported by an operating grant
from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research to MH (CIHR; MOP 89737); MG was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute on Aging, National Institutes of
Health. MH is the CHEO Volunteer Association Endowed Scholar.
Present address: Current address: Atlantic Cancer Research Institute, Hôtel-Dieu Pavilion, 35 Providence St., Moncton, New Brunswick, Canada E1C 8X3.,
Apoptosis Research Centre, Children's Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
Department of Biochemistry, Microbiology and Immunology, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
Department of Paediatrics, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
Laboratory of Cellular and Molecular Biology, Intramural Research Program, National Institute on Aging, National Institutes of Health, Baltimore, MD, USA
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: