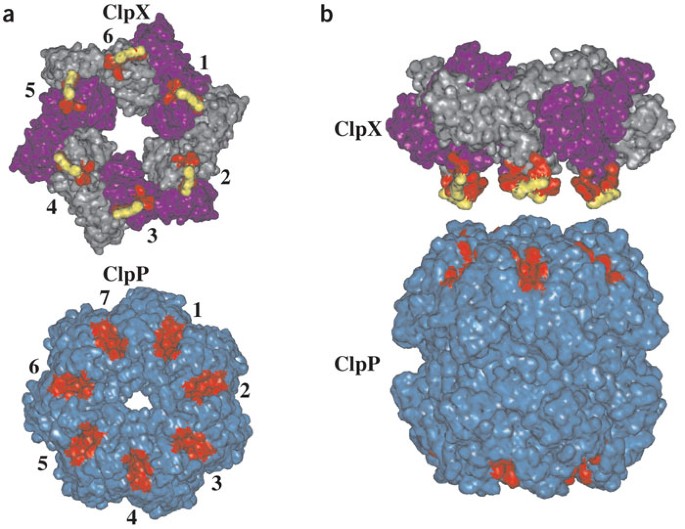
Communication between ClpX and ClpP during substrate processing and degradation
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
In the ClpXP compartmental protease, ring hexamers of the AAA+ ClpX ATPase bind, denature and then translocate protein substrates into the degradation chamber of the double-ring ClpP14
peptidase. A key question is the extent to which functional communication between ClpX and ClpP occurs and is regulated during substrate processing. Here, we show that ClpX-ClpP affinity
varies with the protein-processing task of ClpX and with the catalytic engagement of the active sites of ClpP. Functional communication between symmetry-mismatched ClpXP rings depends on the
ATPase activity of ClpX and seems to be transmitted through structural changes in its IGF loops, which contact ClpP. A conserved arginine in the sensor II helix of ClpX links the nucleotide
state of ClpX to the binding of ClpP and protein substrates. A simple model explains the observed relationships between ATP binding, ATP hydrolysis and functional interactions between ClpX,
protein substrates and ClpP.
We thank S. Boyd, R. Burton, E. Courtenay, C. Farrell, J. Flynn, R. Grant, J. Kenniston, I. Levchenko, S. Siddiqui and D. Wah for discussion and materials, R. Horvitz and J. King for use of
equipment and D. Kim and K. Kim (Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Korea) for the ClpX hexamer coordinates. This work was supported by grants from the US National Institutes of
Health and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI). T. Baker is an employee of HHMI.
Department of Biology, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, 02139, Massachusetts, USA
Shilpa A Joshi, Greg L Hersch, Tania A Baker & Robert T Sauer
Howard Hughes Medical Institute, 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, 02139, Massachusetts, USA
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: