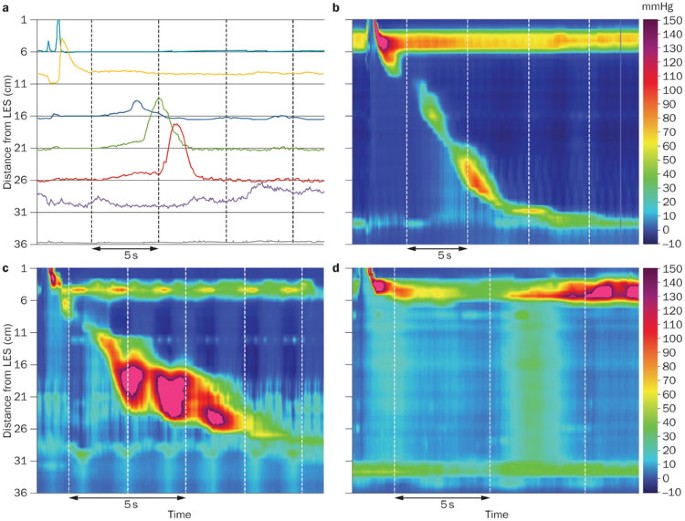
Advances in motility testing—current and novel approaches
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Disorders of gastrointestinal motility are frequently seen in clinical practice. Apart from motility disorders, factors leading to lowered visceroperception thresholds are
recognized as commonly involved in the pathogenesis of functional gastrointestinal disorders. The wide array of gastrointestinal motility and viscerosensitivity tests available is in
contrast with the relatively limited number of tests used universally in clinical practice. The main reason for this discrepancy is that the outcome of a test only becomes truly important
when it carries clinical consequences. The main goal of this Review is to assess the place of the presently available gastrointestinal motility and sensitivity tests in the clinical
armamentarium of the gastroenterologist. KEY POINTS * High-resolution manometry makes the assessment of oesophageal function easier and provides more information than conventional manometry
* Wireless oesophageal pH monitoring provides an opportunity to assess gastro-oesophageal reflux over prolonged periods of time in a patient-friendly fashion * Intraluminal impedance
monitoring of the oesophagus not only enables detection of nonacid reflux, but can also distinguish different belching types * Wireless motility capsule technology has made it possible to
study gastric emptying, small bowel transit and colonic transit in one noninvasive assessment * Several newly developed investigational tools (such as impedance planimetry and colonic
high-resolution manometry) are promising, but their diagnostic value is not yet clear Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via
your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this
article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in
* Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS ASSOCIATIONS AMONG NEUROPHYSIOLOGY MEASURES IN IRRITABLE BOWEL
SYNDROME (IBS) AND THEIR RELEVANCE FOR IBS SYMPTOMS Article Open access 17 June 2020 WEARABLE, EPIDERMAL DEVICES FOR ASSESSMENT OF SWALLOWING FUNCTION Article Open access 20 December 2023
UNDERSTANDING THE PHYSIOLOGY OF HUMAN DEFAECATION AND DISORDERS OF CONTINENCE AND EVACUATION Article 09 August 2021 REFERENCES * Spechler, S. J. & Castell, D. O. Classification of
oesophageal motility abnormalities. _Gut_ 49, 145–151 (2001). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Bredenoord, A. J. _ et al_. Chicago classification criteria of esophageal
motility disorders defined in high resolution esophageal pressure topography. _Neurogastroenterol. Motil._ 24 (Suppl. 1), 57–65 (2012). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Bogte, A.,
Bredenoord, A. J., Oors, J., Siersema, P. D. & Smout, A. J. Relationship between esophageal contraction patterns and clearance of swallowed liquid and solid boluses in healthy controls
and patients with dysphagia. _Neurogastroenterol. Motil._ 24, e364–e372 (2012). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bredenoord, A. J. & Hebbard, G. S. Technical aspects of clinical
high-resolution manometry studies. _Neurogastroenterol. Motil._ 24 (Suppl. 1), 5–10 (2012). PubMed Google Scholar * Tutuian, R. & Castell, D. O. Rumination documented by using combined
multichannel intraluminal impedance and manometry. _Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol._ 2, 340–343 (2004). PubMed Google Scholar * Dent, J. A new technique for continuous sphincter pressure
measurement. _Gastroenterology_ 71, 263–267 (1976). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Clouse, R. E., Staiano, A. & Alrakawi, A. Topographic analysis of esophageal double-peaked waves.
_Gastroenterology_ 118, 469–476 (2000). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ghosh, S. K., Pandolfino, J. E., Zhang, Q., Jarosz, A. & Kahrilas, P. J. Deglutitive upper esophageal sphincter
relaxation: a study of 75 volunteer subjects using solid-state high-resolution manometry. _Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol._ 291, G525–G531 (2006). CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Bredenoord, A. J., Weusten, B. L., Timmer, R. & Smout, A. J. Intermittent spatial separation of diaphragm and lower esophageal sphincter favors acidic and weakly acidic reflux.
_Gastroenterology_ 130, 334–340 (2006). PubMed Google Scholar * Pandolfino, J. E. _ et al_. Achalasia: a new clinically relevant classification by high-resolution manometry.
_Gastroenterology_ 135, 1526–1533 (2008). PubMed Google Scholar * Fox, M. _ et al_. High-resolution manometry predicts the success of oesophageal bolus transport and identifies clinically
important abnormalities not detected by conventional manometry. _Neurogastroenterol. Motil._ 16, 533–542 (2004). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pandolfino, J. E., Fox, M. R., Bredenoord, A.
J. & Kahrilas, P. J. High-resolution manometry in clinical practice: utilizing pressure topography to classify oesophageal motility abnormalities. _Neurogastroenterol. Motil._ 21,
796–806 (2009). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Levine, M. S., Rubesin, S. E. & Laufer, I. Barium esophagography: a study for all seasons. _Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol._
6, 11–25 (2008). PubMed Google Scholar * Pouderoux, P., Shi, G., Tatum, R. P. & Kahrilas, P. J. Esophageal solid bolus transit: studies using concurrent videofluoroscopy and manometry.
_Am. J. Gastroenterol._ 94, 1457–1463 (1999). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Galmiche, J. P. _ et al_. Functional esophageal disorders. _Gastroenterology_ 130, 1459–1465 (2006). PubMed
Google Scholar * El-Takli, I., O'Brien, P. & Paterson, W. G. Clinical diagnosis of achalasia: how reliable is the barium x-ray? _Can. J. Gastroenterol._ 20, 335–337 (2006). CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Rohof, W. O., Lei, A. & Boeckxstaens, G. E. Esophageal stasis on a timed barium esophagogram predicts recurrent symptoms in patients with
long-standing achalasia. _Am. J. Gastroenterol._ 108, 49–55 (2013). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Clouse, R. E., Prakash, C. & Haroian, L. R. Symptom association tests are improved by
the extended ambulatory pH recording time with the Bravo capsule [abstract]. _Gastroenterology_ 124, A537 (2003). Google Scholar * Pandolfino, J. E. _ et al_. Comparison of the Bravo
wireless and Digitrapper catheter-based pH monitoring systems for measuring esophageal acid exposure. _Am. J. Gastroenterol._ 100, 1466–1476 (2005). PubMed Google Scholar * Hakanson, B.
S., Berggren, P., Granqvist, S., Ljungqvist, O. & Thorell, A. Comparison of wireless 48-h (Bravo) versus traditional ambulatory 24-h esophageal pH monitoring. _Scand. J. Gastroenterol._
44, 276–283 (2009). PubMed Google Scholar * Prakash, C. & Clouse, R. E. Value of extended recording time with wireless pH monitoring in evaluating gastroesophageal reflux disease.
_Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol._ 3, 329–334 (2005). PubMed Google Scholar * Sweis, R., Fox, M., Anggiansah, A. & Wong, T. Prolonged, wireless pH-studies have a high diagnostic yield in
patients with reflux symptoms and negative 24-h catheter-based pH-studies. _Neurogastroenterol. Motil._ 23, 419–426 (2011). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wiener, G. J., Richter, J. E.,
Copper, J. B., Wu, W. C. & Castell, D. O. The symptom index: a clinically important parameter of ambulatory 24-hour esophageal pH monitoring. _Am. J. Gastroenterol._ 83, 358–361 (1988).
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Weusten, B. L., Roelofs, J. M., Akkermans, L. M., Berge-Henegouwen, G. P. & Smout, A. J. The symptom-association probability: an improved method for
symptom analysis of 24-hour esophageal pH data. _Gastroenterology_ 107, 1741–1745 (1994). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Silny, J. Intraluminal multiple electric impedance procedure for
measurement of gastrointestinal motility. _J. Gastrointest. Mot._ 3, 151–162 (1991). Google Scholar * Sifrim, D. _ et al_. Acid, nonacid, and gas reflux in patients with gastroesophageal
reflux disease during ambulatory 24-hour pH-impedance recordings. _Gastroenterology_ 120, 1588–1598 (2001). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bredenoord, A. J., Weusten, B. L., Curvers, W. L.,
Timmer, R. & Smout, A. J. Determinants of perception of heartburn and regurgitation. _Gut_ 55, 313–318 (2005). PubMed Google Scholar * Hemmink, G. J. _ et al_. Esophageal pH-impedance
monitoring in patients with therapy-resistant reflux symptoms: 'on' or 'off' proton pump inhibitor? _Am. J. Gastroenterol._ 103, 2446–2453 (2008). PubMed Google Scholar
* Bredenoord, A. J., Weusten, B. L., Sifrim, D., Timmer, R. & Smout, A. J. Aerophagia, gastric, and supragastric belching: a study using intraluminal electrical impedance monitoring.
_Gut_ 53, 1561–1565 (2004). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Hemmink, G. J. _ et al_. Speech therapy in patients with excessive supragastric belching—a pilot study.
_Neurogastroenterol. Motil._ 22, 24–28 (2009). PubMed Google Scholar * Gregersen, H. & Andersen, M. B. Impedance measuring system for quantification of cross-sectional area in the
gastrointestinal tract. _Med. Biol. Eng. Comput._ 29, 108–110 (1991). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * McMahon, B. P. _ et al_. Distensibility testing of the esophagus. _Ann. NY Acad. Sci._
1232, 331–40 (2011). PubMed Google Scholar * Kwiatek, M. A., Pandolfino, J. E., Hirano, I. & Kahrilas, P. J. Esophagogastric junction distensibility assessed with an endoscopic
functional luminal imaging probe (EndoFLIP). _Gastrointest. Endosc._ 72, 272–278 (2010). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * de Ruigh, A. _ et al_. EGJ distensibility as a measure of
treatment outcome in achalasia [abstract]. _Gastroenterology_ 142 (Suppl. 1), S95–S96 (2012). Google Scholar * Kwiatek, M. A. _ et al_. Mechanical properties of the esophagus in
eosinophilic esophagitis. _Gastroenterology_ 140, 82–90 (2011). PubMed Google Scholar * Nasr, I., Attaluri, A., Hashmi, S., Gregersen, H. & Rao, S. S. Investigation of esophageal
sensation and biomechanical properties in functional chest pain. _Neurogastroenterol. Motil._ 22, 520–526 (2010). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Perretta, S., Dallemagne, B.,
McMahon, B., D'Agostino, J. & Marescaux, J. Video. Improving functional esophageal surgery with a “smart” bougie: Endoflip. _Surg. Endosc._ 25, 3109 (2011). PubMed Google Scholar
* Pehlivanov, N., Liu, J., Kassab, G. S., Puckett, J. L. & Mittal, R. K. Relationship between esophageal muscle thickness and intraluminal pressure: an ultrasonographic study. _Am. J.
Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol._ 280, G1093–G1098 (2001). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mittal, R. K. Measuring esophageal distention by high-frequency intraluminal ultrasound probe.
_Am. J. Med._ 115 (Suppl. 3A), 130S–136S (2003). PubMed Google Scholar * Iascone, C., Di, G. E., Maffi, C. & Ruperto, M. Use of radioisotopic esophageal transit in the assessment of
patients with symptoms of reflux and non-specific esophageal motor disorders. _Dis. Esophagus_ 17, 218–222 (2004). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Fass, J. _ et al_. Measuring esophageal
motility with a new intraluminal impedance device. First clinical results in reflux patients. _Scand. J. Gastroenterol._ 29, 693–702 (1994). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Tutuian, R. &
Castell, D. O. Clarification of the esophageal function defect in patients with manometric ineffective esophageal motility: studies using combined impedance-manometry. _Clin. Gastroenterol.
Hepatol._ 2, 230–236 (2004). PubMed Google Scholar * Tutuian, R. & Castell, D. O. Combined multichannel intraluminal impedance and manometry clarifies esophageal function
abnormalities: study in 350 patients. _Am. J. Gastroenterol._ 99, 1011–1019 (2004). PubMed Google Scholar * Tucker, E., Knowles, K., Wright, J. & Fox, M. R. Rumination variations:
aetiology and classification of abnormal behavioural responses to digestive symptoms based on high-resolution manometry studies. _Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther._ 37, 263–274 (2013). CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Bredenoord, A. J. & Smout, A. J. Physiologic and pathologic belching. _Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol._ 5, 772–775 (2007). PubMed Google Scholar * Collins, P. J.,
Horowitz, M., Cook, D. J., Harding, P. E. & Shearman, D. J. Gastric emptying in normal subjects—a reproducible technique using a single scintillation camera and computer system. _Gut_
24, 1117–1125 (1983). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Olausson, E. A. _ et al_. Measurement of gastric emptying by radiopaque markers in patients with diabetes: correlation
with scintigraphy and upper gastrointestinal symptoms. _Neurogastroenterol. Motil._ 25, e224–e232 (2013). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mariani, G. _ et al_. Radionuclide gastroesophageal
motor studies. _J. Nucl. Med._ 45, 1004–1028 (2004). PubMed Google Scholar * Kelly, K. A. Gastric emptying of liquids and solids: roles of proximal and distal stomach. _Am. J. Physiol._
239, G71–G76 (1980). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bharucha, A. E., Camilleri, M., Veil, E., Burton, D. & Zinsmeister, A. R. Comprehensive assessment of gastric emptying with a stable
isotope breath test. _Neurogastroenterol. Motil._ 25, e60–e69 (2013). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Chew, C. G., Bartholomeusz, F. D., Bellon, M. & Chatterton, B. E. Simultaneous
13C/14C dual isotope breath test measurement of gastric emptying of solid and liquid in normal subjects and patients: comparison with scintigraphy. _Nucl. Med. Rev. Cent. East. Eur._ 6,
29–33 (2003). PubMed Google Scholar * Ghoos, Y. F. _ et al_. Measurement of gastric emptying rate of solids by means of a carbon-labeled octanoic acid breath test. _Gastroenterology_ 104,
1640–1647 (1993). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Saad, R. J. & Hasler, W. L. A technical review and clinical assessment of the wireless motility capsule. _Gastroenterol. Hepatol._ 7,
795–804 (2011). Google Scholar * Kuo, B. _ et al_. Comparison of gastric emptying of a nondigestible capsule to a radio-labelled meal in healthy and gastroparetic subjects. _Aliment.
Pharmacol. Ther._ 27, 186–196 (2008). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Sarosiek, I. _ et al_. The assessment of regional gut transit times in healthy controls and patients with gastroparesis
using wireless motility technology. _Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther._ 31, 313–322 (2010). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Minderhoud, I. M., Mundt, M. W., Roelofs, J. M. & Samsom, M. Gastric
emptying of a solid meal starts during meal ingestion: combined study using 13C-octanoic acid breath test and Doppler ultrasonography. Absence of a lag phase in 13C-octanoic acid breath
test. _Digestion_ 70, 55–60 (2004). PubMed Google Scholar * Mundt, M. W., Hausken, T., Smout, A. J. & Samsom, M. Relationships between gastric accommodation and gastrointestinal
sensations in healthy volunteers. A study using the barostat technique and two- and three-dimensional ultrasonography. _Dig. Dis. Sci._ 50, 1654–1660 (2005). CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Stevens, J. E. _ et al_. Measurement of gastric emptying of a high-nutrient liquid by 3D ultrasonography in diabetic gastroparesis. _Neurogastroenterol. Motil._ 23, 220–224 (2011). CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Azpiroz, F. & Malagelada, J. R. Gastric tone measured by an electronic barostat in health and postsurgical gastroparesis. _Gastroenterology_ 92, 934–943 (1987).
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ang, D. Measurement of gastric accommodation: a reappraisal of conventional and emerging modalities. _Neurogastroenterol. Motil._ 23, 287–291 (2011). CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Kuiken, S. D. _ et al_. Development of a test to measure gastric accommodation in humans. _Am. J. Physiol._ 277, G1217–G1221 (1999). CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Bouras, E. P. _ et al_. SPECT imaging of the stomach: comparison with barostat, and effects of sex, age, body mass index, and fundoplication. _Gut_ 51, 781–786 (2002). CAS PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Feinle, C., Kunz, P., Boesiger, P., Fried, M. & Schwizer, W. Scintigraphic validation of a magnetic resonance imaging method to study gastric emptying of a
solid meal in humans. _Gut_ 44, 106–111 (1999). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Sha, W., Pasricha, P. J. & Chen, J. D. Correlations among electrogastrogram, gastric
dysmotility, and duodenal dysmotility in patients with functional dyspepsia. _J. Clin. Gastroenterol._ 43, 716–722 (2009). PubMed Google Scholar * Smout A. J, van der Schee, E. J. &
Grashuis, J. L. What is measured in electrogastrography? _Dig. Dis. Sci._ 25, 179–187 (1980). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Parkman, H. P. & Jones, M. P. Tests of gastric neuromuscular
function. _Gastroenterology_ 136, 1526–1543 (2009). PubMed Google Scholar * Camilleri, M. Study of human gastroduodenojejunal motility. Applied physiology in clinical practice. _Dig. Dis.
Sci._ 38, 785–794 (1993). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Stanghellini, V. _ et al_. Clinical use of manometry for the diagnosis of intestinal motor abnormalities. _Dig. Liver Dis._ 32,
532–541 (2000). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lindberg, G. _ et al_. Full-thickness biopsy findings in chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction and enteric dysmotility. _Gut_ 58, 1084–1090
(2009). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hinton, J. M., Lennard-Jones, J. E. & Young, A. C. A new method for studying gut transit times using radioopaque markers. _Gut_ 10, 842–847 (1969).
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Metcalf, A. M. _ et al_. Simplified assessment of segmental colonic transit. _Gastroenterology_ 92, 40–47 (1987). CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Rao, S. S. _ et al_. Evaluation of gastrointestinal transit in clinical practice: position paper of the American and European Neurogastroenterology and Motility Societies.
_Neurogastroenterol. Motil._ 23, 8–23 (2011). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Tran, K., Brun, R. & Kuo, B. Evaluation of regional and whole gut motility using the wireless motility
capsule: relevance in clinical practice. _Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol._ 5, 249–260 (2012). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Brun, R. _ et al_. Comparative analysis of phase III
migrating motor complexes in stomach and small bowel using wireless motility capsule and antroduodenal manometry. _Neurogastroenterol. Motil._ 24, 332–e165 (2012). CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Vilarino, F. _ et al_. Intestinal motility assessment with video capsule endoscopy: automatic annotation of phasic intestinal contractions. _IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging_ 29, 246–259
(2010). PubMed Google Scholar * Miller, M. A. _ et al_. Comparison of scintigraphy and lactulose breath hydrogen test for assessment of orocecal transit: lactulose accelerates small bowel
transit. _Dig. Dis. Sci._ 42, 10–18 (1997). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Yu, D., Cheeseman, F. & Vanner, S. Combined oro-caecal scintigraphy and lactulose hydrogen breath testing
demonstrate that breath testing detects oro-caecal transit, not small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients with IBS. _Gut_ 60, 334–340 (2011). PubMed Google Scholar * Argenyi, E.
E., Soffer, E. E., Madsen, M. T., Berbaum, K. S. & Walkner, W. O. Scintigraphic evaluation of small bowel transit in healthy subjects: inter- and intrasubject variability. _Am. J.
Gastroenterol._ 90, 938–942 (1995). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bharucha, A. E., Wald, A., Enck, P. & Rao, S. Functional anorectal disorders. _Gastroenterology_ 130, 1510–1518 (2006).
PubMed Google Scholar * Rao, S. S. _ et al_. Minimum standards of anorectal manometry. _Neurogastroenterol. Motil._ 14, 553–559 (2002). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Minguez, M. _ et
al_. Predictive value of the balloon expulsion test for excluding the diagnosis of pelvic floor dyssynergia in constipation. _Gastroenterology_ 126, 57–62 (2004). PubMed Google Scholar *
Ratuapli, S. K., Bharucha, A. E., Noelting, J., Harvey, D. M. & Zinsmeister, A. R. Phenotypic identification and classification of functional defecatory disorders using high-resolution
anorectal manometry. _Gastroenterology_ http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2012.10.049. * Noelting, J. _ et al_. Normal values for high-resolution anorectal manometry in healthy women:
effects of age and significance of rectoanal gradient. _Am. J. Gastroenterol._ 107, 1530–1536 (2012). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Wald, A., Caruana, B. J., Freimanis, M. G.,
Bauman, D. H. & Hinds, J. P. Contributions of evacuation proctography and anorectal manometry to evaluation of adults with constipation and defecatory difficulty. _Dig. Dis. Sci._ 35,
481–487 (1990). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Shorvon, P. J., McHugh, S., Diamant, N. E., Somers, S. & Stevenson, G. W. Defecography in normal volunteers: results and implications.
_Gut_ 30, 1737–1749 (1989). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Fletcher, J. G. _ et al_. Magnetic resonance imaging of anatomic and dynamic defects of the pelvic floor in
defecatory disorders. _Am. J. Gastroenterol._ 98, 399–411 (2003). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bharucha, A. E. & Fletcher, J. G. Recent advances in assessing anorectal structure and
functions. _Gastroenterology_ 133, 1069–1074 (2007). PubMed Google Scholar * Gurland, B. & Hull, T. Transrectal ultrasound, manometry, and pudendal nerve terminal latency studies in
the evaluation of sphincter injuries. _Clin. Colon Rectal Surg._ 21, 157–166 (2008). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Behar, J. _ et al_. Functional gallbladder and sphincter of
oddi disorders. _Gastroenterology_ 130, 1498–1509 (2006). PubMed Google Scholar * Imler, T. D. _ et al_. Low yield of significant findings on endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
in patients with pancreatobiliary pain and no objective findings. _Dig. Dis. Sci._ 57, 3252–3257 (2012). PubMed Google Scholar * Cotton, P. B., Garrow, D. A., Gallagher, J. &
Romagnuolo, J. Risk factors for complications after ERCP: a multivariate analysis of 11,497 procedures over 12 years. _Gastrointest. Endosc._ 70, 80–88 (2009). PubMed Google Scholar *
Craig, A. G. _ et al_. Scintigraphy versus manometry in patients with suspected biliary sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. _Gut_ 52, 352–357 (2003). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
* Delgado-Aros, S., Cremonini, F., Bredenoord, A. J. & Camilleri, M. Does gall-bladder ejection fraction on cholecystokinin cholescintigraphy predict outcome after cholecystectomy in
suspected functional biliary pain? _Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther._ 18, 167–174 (2003). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Barish, M. A., Yucel, E. K. & Ferrucci, J. T. Magnetic resonance
cholangiopancreatography. _N. Engl. J. Med._ 341, 258–264 (1999). CAS PubMed Google Scholar Download references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of
Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Academic Medical Center, Meibergdreef 9, Amsterdam, 1100 DE, the Netherlands Albert J. Bredenoord & André J. P. M. Smout Authors * Albert J. Bredenoord
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * André J. P. M. Smout View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS The authors contributed equally to all aspects of this article. CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to André J. P. M. Smout. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS A.
J. Bredenoord has received research funding from Shire–Movetis NV and Endostim and received payment from MMS International for development of educational presentations. A. J. P. M. Smout has
received sponsorship from Shire–Movetis NV, MMS international and Given Imaging for an educational meeting on motility testing. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS
ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Bredenoord, A., Smout, A. Advances in motility testing—current and novel approaches. _Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol_ 10, 463–472 (2013).
https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2013.80 Download citation * Published: 07 May 2013 * Issue Date: August 2013 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2013.80 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you
share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the
Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative