A molecular light switch turns off neural activity
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
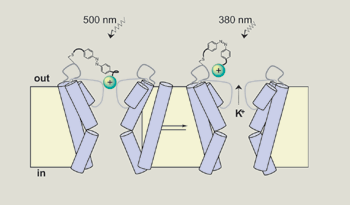
Access through your institution Buy or subscribe Voltage-gated potassium channels can be blocked by quaternary ammonium (QA) ions that bind to amino acids in the pore-lining region. Kramer
and colleagues synthesized a tether attached to a QA group, which can covalently bind to a potassium channel that the authors modified to make the QA blocker the primary determinant of its
gating. A section of the tether is photoisomerizable, meaning that its conformation can be changed by light. Shining light of a long wavelength (500 nm) shifts the tether into a long form,
whereas light of a shorter wavelength (380 nm) shifts it to a shorter form. In the long form, the attached QA group can access and block the potassium channel pore, turning the channel off,
but in the short form, the QA group does not reach the channel, allowing potassium ions to flow out of the cell. Because potassium efflux causes neurons to become hyperpolarized, the
short-wavelength light can silence activity in hippocampal neurons exogenously expressing the SPARK channels. This new technique should find wide applicability in studies of circuit function
and in other manipulations of neuronal activity. In addition, it should spark the development of more experimental, and perhaps therapeutic, tools. This is a preview of subscription
content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue
Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL
ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support Authors * Cara Allen View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Allen, C. A molecular light switch turns off neural activity. _Nat
Neurosci_ 7, 1291 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1204-1291 Download citation * Issue Date: 01 December 2004 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1204-1291 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share
the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer
Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative