Quantifying force-dependent and zero-force dna intercalation by single-molecule stretching
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
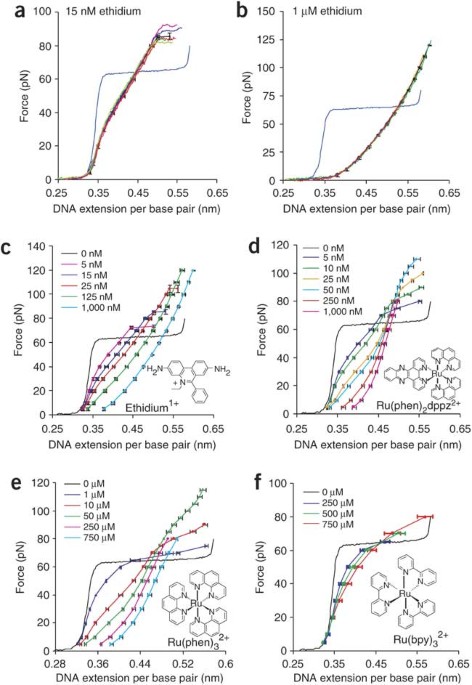
ABSTRACT We used single DNA molecule stretching to investigate DNA intercalation by ethidium and three ruthenium complexes. By measuring ligand-induced DNA elongation at different ligand
concentrations, we determined the binding constant and site size as a function of force. Both quantities depend strongly on force and, in the limit of zero force, converge to the known bulk
solution values, when available. This approach allowed us to distinguish the intercalative mode of ligand binding from other binding modes and allowed characterization of intercalation with
binding constants ranging over almost six orders of magnitude, including ligands that do not intercalate under experimentally accessible solution conditions. As ligand concentration
increased, the DNA stretching curves saturated at the maximum amount of ligand intercalation. The results showed that the applied force partially relieves normal intercalation constraints.
We also characterized the flexibility of intercalator-saturated dsDNA for the first time. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access
via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy
this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: *
Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS DNA CALORIMETRIC FORCE SPECTROSCOPY AT SINGLE BASE PAIR
RESOLUTION Article Open access 19 March 2025 PREDICTING THE EFFECT OF BINDING MOLECULES ON THE SHAPE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF STRUCTURED DNA ASSEMBLIES Article Open access 31 July 2024
HIGH-THROUGHPUT SINGLE-MOLECULE QUANTIFICATION OF INDIVIDUAL BASE STACKING ENERGIES IN NUCLEIC ACIDS Article Open access 06 February 2023 REFERENCES * Lerman, L.S. Structural considerations
in the interaction of DNA and acridines. _J. Mol. Biol._ 3, 18–30 (1961). Article CAS Google Scholar * Waring, M.J. DNA Modification and cancer. _Annu. Rev. Biochem._ 50, 159–192 (1981).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Hurley, L.H. DNA and its associated processes as targets for cancer therapy. _Nat. Rev. Cancer_ 2, 188–200 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar * Mihailovic,
A. et al. Exploring the interaction of ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes with DNA using single-molecule techniques. _Langmuir_ 22, 4699–4709 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Vladescu, I.D., McCauley, M.J., Rouzina, I. & Williams, M.C. Mapping the phase diagram of single DNA molecule force-induced melting in the presence of ethidium. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 95,
158102 (2005). Article Google Scholar * Berman, H.M. & Young, P.R. The interaction of intercalating drugs with nucleic acids. _Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng._ 10, 87–114 (1981). Article
CAS Google Scholar * Haq, I. et al. Interaction of delta- and lambda-[Ru(phen)2DPPZ]2+ with DNA: a calorimetric and equilibrium binding study. _J. Am. Chem. Soc._ 117, 4788–4796 (1995).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Dupureur, C.M. & Barton, J.K. Structural studies of lambda- and delta-[Ru(phen)2dppz]2+ bound to (GTCGAC)2: characterization of enantioselective
intercalation. _Inorg. Chem._ 36, 33–43 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lincoln, P. & Nordén, B. DNA binding geometries of ruthenium(II) complexes with 1,10-phenanthroline and
2,2′-bipyridine ligands studied with linear dichroism spectroscopy. Borderline cases of intercalation. _J. Phys. Chem. B_ 102, 9583–9594 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Satyanarayana, S., Dabrowaik, J.C. & Chaires, J.B. Neither delta- nor lambda-Tris(phenanthroline)ruthenium(II) binds to DNA by classical intercalation. _Biochemistry_ 31, 9319–9324
(1992). Article CAS Google Scholar * Pyle, A.M. et al. Mixed-ligand complexes of ruthenium(II): factors governing binding to DNA. _J. Am. Chem. Soc._ 111, 3051–3058 (1989). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Cluzel, P. et al. DNA: an extensible molecule. _Science_ 271, 792–794 (1996). Article CAS Google Scholar * McCauley, M.J. & Williams, M.C. Mechanisms of DNA binding
determined in optical tweezers experiments. _Biopolymers_ 85, 154–168 (2007). Article CAS Google Scholar * McGhee, J.D. & von Hippel, P.H. Theoretical aspects of DNA-protein
interactions: cooperative and non-cooperative binding of large ligands to a one-dimensional homogeneous lattice. _J. Mol. Biol._ 86, 469–489 (1974). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Mahadevan, S. & Palaniandavar, M. Chiral discrimination in the binding of tris(phenanthroline)ruthenium(II) to calf thymus DNA: an electrochemical study. _Bioconjug. Chem._ 7, 138–143
(1996). Article CAS Google Scholar * Baumann, C.G. et al. Stretching of single collapsed DNA molecules. _Biophys. J._ 78, 1965–1978 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Cruceanu, M. et
al. Nucleic acid binding and chaperone properties of HIV-1 Gag and nucleocapsid proteins. _Nucleic Acids Res._ 34, 593–605 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar * Record, M.T., Jr, Lohman,
T.M. & de Haseth, P.L. Ion effects on ligand-nucleic acid interactions. _J. Mol. Biol._ 107, 145–158 (1976). Article CAS Google Scholar * Makhatadze, G.I. & Privalov, P.L.
Energetics of protein structure. _Adv. Prot. Chem._ 47, 307–425 (1995). CAS Google Scholar * Phillips, T., Rajput, C., Twyman, L., Haq, I. & Thomas, J.A. Water-soluble organic dppz
analogues–tuning DNA binding affinities, luminescence, and photo-redox properties. _Chem. Commun. (Camb.)_ 4327–4329 (2005). * Smith, S.B., Cui, Y.J. & Bustamante, C. Overstretching
B-DNA: The elastic response of individual double-stranded and single-stranded DNA molecules. _Science_ 271, 795–799 (1996). Article CAS Google Scholar * McCauley, M., Hardwidge, P.R.,
Maher, L.J., III & Williams, M.C. Dual binding modes for an HMG domain from human HMGB2 on DNA. _Biophys. J._ 89, 353–364 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Phillips, T. et al. DNA
binding of an organic dppz-based intercalator. _Biochemistry_ 43, 13657–13665 (2004). Article CAS Google Scholar * Chaires, J.B. Drug–DNA interactions. _Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol._ 8,
314–320 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Shokri, L., Marintcheva, B., Richardson, C.C., Rouzina, I. & Williams, M.C. Single-molecule force spectroscopy of salt-dependent
bacteriophage T7 gene 2.5 protein binding to single-stranded DNA. _J. Biol. Chem._ 281, 38689–38696 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar * Westerlund, F., Eng, M.P., Winters, M.U. &
Lincoln, P. Binding geometry and photophysical properties of DNA-threading binuclear ruthenium complexes. _J. Phys. Chem. B_ 111, 310–317 (2007). Article CAS Google Scholar * Nordmeier,
E. Absorption spectroscopy and dynamic and static light-scattering studies of ethidium bromide binding to calf thymus DNA: implications for outside binding and intercalation. _J. Phys.
Chem._ 96, 6045–6055 (1992). Article CAS Google Scholar * Jain, S.C. & Sobell, H.M. Visualization of drug-nucleic acid interactions at atomic resolution. VII. Structure of an
ethidium/dinucleoside monophosphate crystalline complex, ethidium: uridylyl(3′-5′) adenosine. _J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn._ 1, 1161–1177 (1984). Article CAS Google Scholar * Vardevanyan,
P.O., Antonyan, A.P., Parsadanyan, M.A., Davtyan, H.G. & Karapetyan, A.T. The binding of ethidium bromide with DNA: interaction with single- and double-stranded structures. _Exp. Mol.
Med._ 35, 527–533 (2003). Article CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We acknowledge funding from the US National Science Foundation (MCB0238190), US National
Institutes of Health (GM072462) and American Chemical Society Petroleum Research Fund. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Physics, Northeastern University, Boston,
02115, Massachusetts, USA Ioana D Vladescu, Micah J McCauley & Mark C Williams * Department of Chemistry, Mount Holyoke College, South Hadley, 01075, Massachusetts, USA Megan E Nuñez *
Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Biophysics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, 55455, Minnesota, USA Ioulia Rouzina * Center for Interdisciplinary Research on Complex
Systems, Northeastern University, Boston, 02115, Massachusetts, USA Mark C Williams Authors * Ioana D Vladescu View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * Micah J McCauley View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Megan E Nuñez View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Ioulia Rouzina View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Mark C Williams View author publications You can also search
for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS I.D.V. performed most experiments. M.J.M. maintained the instrument, labeled DNA and performed some experiments. M.E.N. provided
ruthenium compounds. I.D.V., I.R., M.E.N. and M.C.W. designed the research. I.R. developed the theory. I.D.V., M.E.N., I.R. and M.C.W. wrote the paper. CORRESPONDING AUTHORS Correspondence
to Ioulia Rouzina or Mark C Williams. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing financial interests. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. 1 Drug effect
on hysteresis behavior. (PDF 92 kb) SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. 2 Dependence of Ru(phen)2dppz2+ binding on force. (PDF 81 kb) SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. 3 Dependence of Ru(phen)32+ binding on force. (PDF 77
kb) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Vladescu, I., McCauley, M., Nuñez, M. _et al._ Quantifying force-dependent and zero-force DNA
intercalation by single-molecule stretching. _Nat Methods_ 4, 517–522 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth1044 Download citation * Received: 29 January 2007 * Accepted: 21 March 2007 *
Published: 29 April 2007 * Issue Date: June 2007 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth1044 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get
shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative