Genetic manipulation of adult mouse neurogenic niches by in vivo electroporation
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
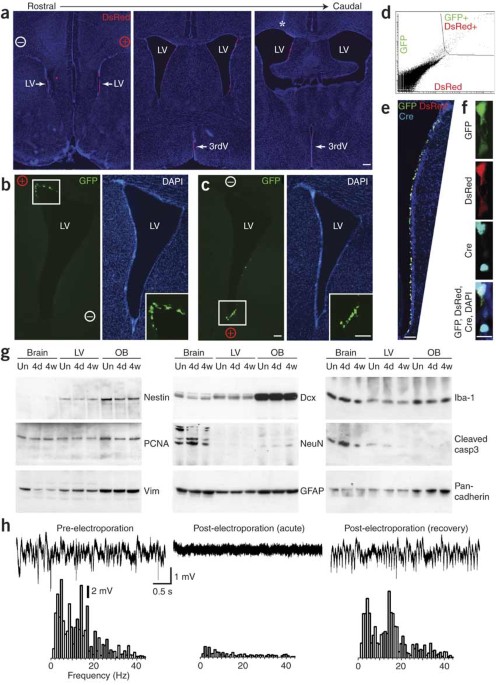
Targeted ectopic expression of genes in the adult brain is an invaluable approach for studying many biological processes. This can be accomplished by generating transgenic mice or by virally
mediated gene transfer, but these methods are costly and labor intensive. We devised a rapid strategy that allows localized in vivo transfection of plasmid DNA within the adult neurogenic
niches without detectable brain damage. Injection of plasmid DNA into the ventricular system or directly into the hippocampus of adult mice, followed by application of electrical current via
external electrodes, resulted in transfection of neural stem or progenitor cells and mature neurons. We showed that this strategy can be used for both fate mapping and gain- or
loss-of-function experiments. Using this approach, we identified an essential role for cadherins in maintaining the integrity of the lateral ventricle wall. Thus, in vivo electroporation
provides a new approach to study the adult brain.
We thank R. Kageyama (Kyoto University) for the gift of the nestin promoter vector30, C. Ibáñez (Karolinska Institutet) for the gift of a BDNF expression plasmid, M. Wheelock (University of
Nebraska Medical Center) for providing the dominant-negative N-cadherin cDNA and K. Fernandes (University of Montreal) for critically reading the manuscript. This study was supported by
grants from the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Cancer Society, the Foundation for Strategic Research, the Karolinska Institutet, Tobias Stiftelsen and the European Commission
Framework VI Programme, EuroStemCell. F.B.-H. is supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
Present address: Present address: The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 43 Vassar Street, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139, USA.,
Department of Cell and Molecular Biology, Medical Nobel Institute, Stockholm, SE-171 77, Sweden
Fanie Barnabé-Heider, Konstantinos Meletis, Malin Eriksson, Olaf Bergmann, Hanna Sabelström, Harald Mikkers & Jonas Frisén
Department of Neuroscience, Box 285, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, SE-171 77, Sweden
Department of Molecular Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine Program, Leiden University Medical Center, P.O. Box 9600, RC Leiden, 2300, The Netherlands
F.B.-H. designed, performed and analyzed the study and wrote the manuscript; K.M. designed and performed most parts of the study; M.E. performed and analyzed part of the study (including BAC
analysis); O.B. performed part of the study; H.S. performed and analyzed part of the study; M.A.H. performed EEG analysis; H.M. designed and performed part of the adenoviral study; and J.F.
designed the study and wrote the manuscript.
Supplementary Figures 1–3, Supplementary Methods (PDF 435 kb)
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: