Hepatitis B and C in children | Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Chronic infection with hepatitis B affects nearly 350 million individuals worldwide and is the leading cause of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver cirrhosis. Universal infant
immunization has decreased rates of HBV infection, although transmission continues to occur via vertical (mother-to-child) and horizontal (sexual, parenteral and household) routes.
Treatments are now available for children with chronic HBV infection, but appropriate selection of those most likely to respond to treatment is important. Interferon _α_ and lamivudine are
currently approved in the US for the treatment of children older than 2 years of age who have chronic HBV infection. Hepatitis C infection affects almost 170 million individuals worldwide.
Of individuals exposed to HCV, 60–80% develop chronic hepatitis, and 10–15% of those chronically infected develop cirrhosis within several decades. No vaccine exists for HCV; therefore,
prevention of parenteral transmission is important. A high index of suspicion is essential for the diagnosis of HCV infection given its silent clinical presentation. Appropriate evaluation
of infected individuals is warranted when considering their suitability for therapy. Interferon _α_ and ribavirin, used in combination, are currently approved in the US for the treatment of
children older than 3 years of age with chronic HCV infection. KEY POINTS * The implementation of universal infant hepatitis B immunization has reduced vertical transmission rates by 85–90%,
and has similarly reduced the rates of hepatocellular carcinoma due to hepatitis B * Without prophylaxis, neonates exposed to HBV have a greater than 90% risk of developing chronic
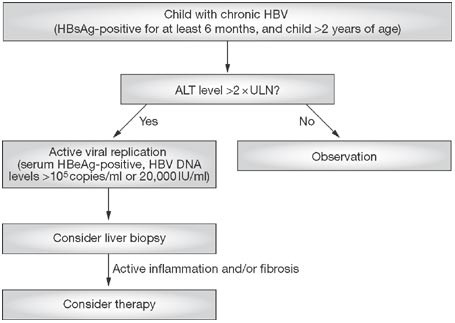
infection, in comparison to adults, who, when exposed, only have a 2–10% risk of developing chronic infection * Determination of active viral infection and associated hepatocellular
inflammation is important when considering antiviral therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis B * HCV infection usually occurs without symptoms, and most infected individuals develop
chronic infection * HCV genotype is important in the prediction of treatment response to antiviral therapy * Liver biopsy is imperative to determine the degree of hepatocellular injury from
chronic hepatitis C Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution
Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full
article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs *
Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS HEPATITIS A VIRUS INFECTION Article 28 September 2023 GLOBAL BURDEN OF HEPATITIS B VIRUS: CURRENT STATUS, MISSED OPPORTUNITIES
AND A CALL FOR ACTION Article 06 April 2023 PREVALENCE, INCIDENCE, AND OUTCOMES OF HEPATITIS E VIRUS COINFECTION IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC HEPATITIS C Article Open access 21 August 2023
REFERENCES * Chang M-H (2001) Viral hepatitis and its prevention in children. In Viral and Nonviral Liver Infections. _Intl Sem Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr_ 10: 1–7 Article Google Scholar *
Mast EE _ et al_. (1999) Strategies to prevent and control hepatitis B and C virus infections: a global perspective. _Vaccine_ 17: 1730–1733 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * World
Health Organization (2000) Fact sheet no 204: hepatitis B. Geneva: World Health Organization * McQuillan GM _ et al_. (1999) Prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection in the United States:
the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 1976–1994. _Am J Public Health_ 89: 14–18 Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Goldstein ST _ et al_. (2002)
Incidence and risk factors for acute hepatitis B in the United States, 1982–1998: implications for vaccination programs. _J Infect Dis_ 185: 713–719 Article PubMed Google Scholar *
Kidd-Ljunggren K _ et al_. (2006) High levels of hepatitis B virus DNA in bodyfluids from chronic carriers. _J Hosp Infect_ 64: 352–357 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Diel R _ et
al_. (2005) Transmission of hepatitis B in Hamburg, Germany, 1998–2002: a prospective, population-based study. _Med Microbiol Immunol_ 194: 193–199 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Hahne S _ et al_. (2004) Incidence and routes of transmission of hepatitis B virus in England and Wales, 1995–2000: implications for immunization policy. _J Clin Virol_ 29: 211–220 Article
PubMed Google Scholar * Khan AJ _ et al_. (2005) Ongoing transmission of hepatitis B virus infection among inmates at a state correctional facility. _Am J Public Health_ 95: 1793–1799
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Doganci T _ et al_. (2005) Horizontal transmission of hepatitis B virus in children with chronic hepatitis B. _World J Gastroenterol_ 11:
418–420 Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Lobato C _ et al_. (2006) Intrafamilial prevalence of hepatitis B virus in western Brazilian amazon region: epidemiologic and
biomolecular study. _J Gastroenterol Hepatol_ 21: 863–868 Article PubMed Google Scholar * Stevens CE _ et al_. (1975) Vertical transmission of hepatitis B antigen in Taiwan. _N Engl J
Med_ 292: 771–774 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hill JB _ et al_. (2002) Risk of hepatitis B transmission in breast-fed infants of chronic hepatitis B carriers. _Obstet Gynecol_
99: 1049–1052 PubMed Google Scholar * Wang JS _ et al_. (2003) Breastfeeding does not pose any additional risk of immunoprophylaxis failure on infants of HBV carrier mothers. _Int J Clin
Pract_ 57: 100–102 CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Liu CJ _ et al_. (2006) Transmission of occult hepatitis B virus by transfusion to adult and pediatric recipients in Taiwan. _J Hepatol_ 44:
39–46 Article PubMed Google Scholar * Gacic-Dobo M _ et al_. (2003) Global progress toward universal childhood hepatitis B vaccination, 2003. _Morb Mortal Wkly Rep_ 52: 868–870 Google
Scholar * World Health Organization (2002) WHO vaccine preventable diseases monitoring system: 2002 global summary. Report No.: WHO/V&B/02.20. Geneva: World Health Organization * Chien
YC _ et al_. (2006) Nationwide hepatitis B vaccination program in Taiwan: effectiveness in the 20 years after it was launched. _Epidemiol Rev_ 28: 126–135 Article PubMed Google Scholar *
Chang MH _ et al_. (1997) Universal hepatitis B vaccination in Taiwan and the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in children. _N Engl J Med_ 336: 1855–1859 Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Perz JF _ et al_. (2006) Near elimination of hepatitis B virus infections among Hawaii elementary school children after universal infant hepatitis B vaccination. _Pediatrics_ 118:
1403–1408 Article PubMed Google Scholar * Katkov WN and Dienstag JL (1995) Hepatitis vaccines. _Gastroenterol Clin North Am_ 24: 147–159 CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Greenberg DP
(1993) Pediatric experience with recombinant hepatitis B vaccines and relevant safety and immunogenicity studies. _Pediatr Infect Dis J_ 12: 438–445 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Zanetti AR _ et al_. (2005) Long-term immunogenicity of hepatitis B vaccination and policy for booster: an Italian multicenter study. _Lancet_ 366: 1337–1338 Article CAS Google Scholar *
Doo E (2003) Epidemiology and immunopathogenesis of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. _Curr Hep Rep_ 2: 79–81 Article Google Scholar * Shiraki K _ et al_. (1980) Acute hepatitis B in
infants born to carrier mother with the antibody to hepatitis B e antigen. _J Pediatr_ 97: 768–770 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bortolotti F (1996) Chronic viral hepatitis in
childhood. _Clin Gastroenterol_ 10: 185–206 CAS Google Scholar * Boxall EH _ et al_. (2004) Natural history of hepatitis B in perinatally infected carriers. _Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal
Ed_ 89: F456–F460 Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Huo T-I _ et al_. (1998) Sero-clearance of hepatitis B surface antigen in chronic carriers does not necessarily
imply a good prognosis. _Hepatology_ 28: 231–236 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lok ASF and McMahon BJ (2007) AASLD practice guidelines: chronic hepatitis B. _Hepatology_ 45:
507–539 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wu TC _ et al_. (1987) Primary hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B infection during childhood. _Hepatology_ 7: 46–48 Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Czauderna P _ et al_. (2002) Hepatocellular carcinoma in children: results of the first prospective study of the International Society of Pediatric Oncology Group. _J
Clin Oncol_ 20: 2798–2804 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Keeffe EB (1999) Vaccination against hepatitis A and B in chronic liver disease. _Viral Hepatitis Rev_ 5: 77–88 Google
Scholar * Broderick A and Jonas MM (2004) Management of hepatitis B in children. _Clin Liver Dis_ 8: 387–401 Article PubMed Google Scholar * Kelly D (2006) Viral hepatitis B and C in
children. _J Royal Soc Med_ 99: 353–357 Article Google Scholar * Jonas M _ et al_. (2002) Clinical trial of lamivudine in children with chronic hepatitis B. _N Engl J Med_ 346: 1706–1713
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Selimoglu MA _ et al_. (2002) Alpha interferon and lamivudine combination therapy for chronic hepatitis B in children. _Pediatr Int_ 44: 404–408
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Fontana RJ (1999) Antivirals in hepatitis B. _Clin Perspec Gastroenterol_ 2: 207–213 Google Scholar * Jonas MM (1996) Hepatitis C virus infection:
clinical aspects and treatment with interferon alfa. _Clin Ther_ 18 (Suppl B): S110–S125 Article Google Scholar * Sokal EM _ et al_. (1998) Interferon alfa therapy for chronic hepatitis B
in children: a multinational randomized controlled trial. _Gastroenterology_ 114: 988–995 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Renault PF _ et al_. (1987) Psychiatric complications of
long-term interferon alpha therapy. _Arch Intern Med_ 147: 1577–1580 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Sokal EM _ et al_. (2006) Long term lamivudine therapy for children with
HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. _Hepatology_ 43: 225–232 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hartman C _ et al_. (2003) Lamivudine treatment for chronic hepatitis B infection in
children unresponsive to interferon. _Pediatr Inf Dis J_ 22: 224–228 Google Scholar * Dikici B _ et al_. (2004) Current therapeutic approaches in childhood chronic hepatitis B infection: a
multicenter study. _J Gastroenterol Hepatol_ 19: 127–133 Article PubMed Google Scholar * D'Antiga L _ et al_. (2006) Combined lamivudine/interferon alfa treatment in immune tolerant
children perinatally infected with hepatitis B: a pilot study. _J Pediatr_ 148: 228–233 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lau GK _ et al_. (2005) Peginterferon alfa2a, lamivudine, and
the combination for HBeAG-positive chronic hepatitis B. _N Engl J Med_ 352: 2682–2695 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Perillo R _ et al_. (1999) _In vivo_ demonstration of
sensitivity of YMDD variants to adefovir. _Gastroenterology_ 116A: 1261 Google Scholar * Min AD and Dienstag JL (2007) Oral antivirals for chronic hepatitis B. _Clin Liver Dis_ 11: 851–868
Article PubMed Google Scholar * Wong W and Terrault N (2005) Update on chronic hepatitis C. _Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol_ 3: 507–520 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Strader DB _ et
al_. (2004) AASLD practice guideline: diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C. _Hepatology_ 39: 1147–1171 Article PubMed Google Scholar * Alter MJ _ et al_. (1999) The
prevalence of hepatitis C infection in the United States, 1988 through 1994. _N Engl J Med_ 341: 556–562 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gibb DM _ et al_. (2000) Active surveillance
of hepatitis C infection in the UK and Ireland. _Arch Dis Child_ 82: 286–291 Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Hsu EK and Murray KF (2007) Hepatitis C virus in
children. _J Pediatr Infect Dis_ 2: 3–9 Article Google Scholar * European Association for the Study of the Liver (1999) International consensus conference on hepatitis C. _J Hepatol_ 31
(Suppl 1): S3–S8 * Bortolotti F _ et al_. (2001) An epidemiological survey of hepatitis C virus infection in Italian children in the decade 1990–1999. _J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr_ 32:
562–566 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gibb DM _ et al_. (2000) Mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis C virus: evidence for preventable peripartum transmission. _Lancet_ 356:
904–907 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Zanetti AR _ et al_. (1998) A prospective study on mother-to-infant transmission of hepatitis C virus. _Intervirology_ 41: 208–212 Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Tovo PA _ et al_. for the Italian Study Group for HCV Infection in Children (1997) Increased risk of maternal-infant hepatitis C virus transmission for women
coinfected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. _Clin Infect Dis_ 25: 1121–1124 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * England K _ et al_. (2006) Vertically acquired pediatric
coinfection with HIV and hepatitis C virus. _Lancet Infect Dis_ 6: 83–90 Article PubMed Google Scholar * Mok J _ et al_. (2005) When does mother to child transmission of hepatitis C virus
occur. _Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed_ 90: F156–F160 Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Ruiz-Extremera A _ et al_. (2000) Follow-up of transmission of hepatitis C to
babies of human immunodeficiency virus-negative women: the role of breast-feeding in transmission. _Pediatr Infect Dis J_ 19: 511–516 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Airoldi J
(2006) Hepatitis C and pregnancy. _Obstet Gynecol Surv_ 61: 666–672 Article PubMed Google Scholar * American Academy of Pediatrics (2006) Hepatitis C. In: _Red Book: 2006 report of the
Committee on Infectious Diseases_, edn 27, 355–359 (Eds Pickering LK. _ et al_.) Elk Grove Village: American Academy of Pediatrics * Mast EE _ et al_. (2005) Risk factors for perinatal
transmission of hepatitis C virus (HCV) and the natural history of HCV infection acquired in infancy. _J Infect Dis_ 192: 1880–1889 Article PubMed Google Scholar * Vogt M _ et al_. (1999)
Prevalence and clinical outcome of hepatitis C infection in children who underwent cardiac surgery before the implementation of blood-donor screening. _N Engl J Med_ 341: 866–870 Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Davison SM _ et al_. (2006) Perinatal hepatitis C virus infection: diagnosis and management. _Arch Dis Child_ 91: 781–785 Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Feld JJ and Liang TJ (2006) Hepatitis C—identifying patients with progressive liver injury. _Hepatology_ 43 (Suppl 1): S194–S206 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Chen SL and Morgan TR (2006) The natural history of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. _Int J Med Sci_ 3: 47–52 Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Murray KF _ et al_. (2005)
Liver histology and alanine amino transferase levels in children and adults with chronic hepatitis C infection. _J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr_ 41: 634–638 Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Hoshiyama A _ et al_. (2000) Clinical and histologic features of chronic hepatitis C virus infection after blood transfusion in Japanese children. _Pediatrics_ 105: 62–65 Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Zellos A _ et al_. (1999) High viral load and mild liver injury in children with hemophilia compared with other children with chronic hepatitis C virus
infection. _J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr_ 29: 418–423 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Birnbaum AH _ et al_. (2000) Hepatitis C in children. _N Engl J Med_ 342: 290–292 Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Ferenci P _ et al_. (2005) Predicting sustained virological responses in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with peginterferon alfa-2a (40 KD)/ribavirin. _J
Hepatol_ 43: 425–433 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Rizzetto M (2004) Treatment of hepatitis C virus genotype 2 or 3 with pegylated interferon plus ribavirin. _J Hepatol_ 42:
275–278 Article Google Scholar * Murray KF _ et al_. (2007) Design of the PEDS-C trial: pegylated interferon +/− ribavirin for children with chronic hepatitis C viral infection. _Clin
Trials_ 4: 661–673 Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Manns MP _ et al_. (2001) Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for
initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. _Lancet_ 22: 958–965 Article Google Scholar * Fried MW _ et al_. (2002) Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic
hepatitis C virus infection. _N Engl J Med_ 347: 975–982 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * González-Peralta RP _ et al_. (2005) Interferon alfa-2b with ribavirin for children with
chronic hepatitis C: efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics. _Hepatology_ 42: 1010–1018 Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar * Pawlotsky J-M (2000) Hepatitis C virus resistance to antiviral
therapy. _Hepatology_ 32: 889–896 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lackner H _ et al_. (2000) Interferon-alpha and ribavirin in treating children and young adults with chronic
hepatitis C after malignancy. _Pediatrics_ 106: 1–4 Article Google Scholar * Suoglu OD _ et al_. (2002) Does interferon and ribavirin combination therapy increase the rate of treatment
response in children with hepatitis C. _J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr_ 34: 199–206 Article CAS Google Scholar * Hartman C _ et al_. (2003) The effect of early treatment in children with
chronic hepatitis. _J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr_ 37: 252–257 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Figlerowicz M _ et al_. (2004) Interferon alpha and ribavirin in the treatment of
children with chronic hepatitis C. _Eur J Pediatr_ 1633: 265–267 Article Google Scholar * Wirth S _ et al_. (2002) Recombinant alfa-interferon plus ribavirin therapy in children and
adolescents with chronic hepatitis C. _Hepatology_ 36: 1280–1284 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Vajro P _ et al_. (1998) Interferon: a meta-analysis of published studies in
pediatric chronic hepatitis B. _Acta Gastroenterol Belg_ 61: 219–223 CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Torre D and Tambini R (1996) Interferon-alpha therapy for chronic hepatitis B in children:
a meta-analysis. _Clin Infect Dis_ 23: 131–137 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Cooksley WGE _ et al_. (2003) Peginterferon alfa-2a (40kDa): an advance in the treatment of hepatitis
B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. _J Vir Hepat_ 10: 298–305 Article CAS Google Scholar * Wong DKH _ et al_. (1993) Effect of alpha-interferon treatment in patients with hepatitis
B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. _Ann Intern Med_ 119: 312–323 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Marcellin P _ et al_. (2007) 76 week follow up of HBeAg positive chronic
hepatitis B patients treated with telbivudine, adefovir or switched from adefovir to telbivudine. _J Hepatol_ 46 (Suppl 1): S55 Article Google Scholar * Schwarz KB _ et al_. (2003) The
safety, efficacy and pharmacokinetics of peginterferon alfa-2a (40kD) in children with chronic hepatitis C. _Gastroenterology_ 124 (Suppl 1): A700 Article Google Scholar * Wirth S _ et
al_. (2005) Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin treatment in children and adolescents with chronic hepatitis C. _Hepatology_ 41: 1013–1018 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Download
references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Division of Gastroenterology and Nutrition, EK Hsu is a first year Fellow in Pediatric Gastroenterology at The Children's
Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, and KF Murray is Director of the Hepatobiliary Program, Children's Hospital and Regional Medical Center, Seattle, WA, USA., Evelyn K Hsu
& Karen F Murray Authors * Evelyn K Hsu View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Karen F Murray View author publications You can also search
for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Karen F Murray. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS Karen F Murray has received grant/research support
from Gilead, Roche and Schering-Plough. Evelyn K Hsu declared no competing interests. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Hsu, E., Murray, K.
Hepatitis B and C in children. _Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol_ 5, 311–320 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpgasthep1124 Download citation * Received: 28 March 2007 * Accepted: 21 February
2008 * Published: 15 April 2008 * Issue Date: June 2008 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpgasthep1124 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this
content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative