Cooperative demethylation by jmjd2c and lsd1 promotes androgen receptor-dependent gene expression
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Posttranslational modifications of histones, such as methylation, regulate chromatin structure and gene expression1. Recently, lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1)2, the first
histone demethylase, was identified. LSD1 interacts with the androgen receptor and promotes androgen-dependent transcription of target genes by ligand-induced demethylation of mono- and
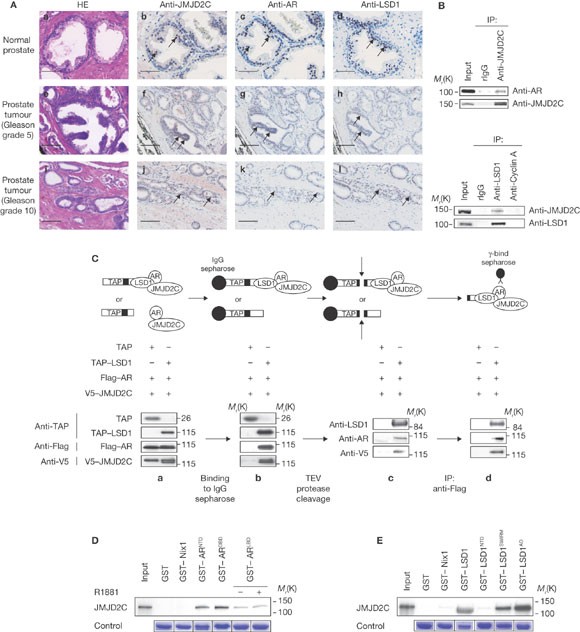
dimethylated histone H3 at Lys 9 (H3K9)3 only. Here, we identify the Jumonji C (JMJC)4 domain-containing protein JMJD2C5,6 as the first histone tridemethylase regulating androgen receptor
function. JMJD2C interacts with androgen receptor _in vitro_ and _in vivo_. Assembly of ligand-bound androgen receptor and JMJD2C on androgen receptor-target genes results in demethylation
of trimethyl H3K9 and in stimulation of androgen receptor-dependent transcription. Conversely, knockdown of JMJD2C inhibits androgen-induced removal of trimethyl H3K9, transcriptional
activation and tumour cell proliferation. Importantly, JMJD2C colocalizes with androgen receptor and LSD1 in normal prostate and in prostate carcinomas. JMJD2C and LSD1 interact and both
demethylases cooperatively stimulate androgen receptor-dependent gene transcription. In addition, androgen receptor, JMJD2C and LSD1 assemble on chromatin to remove methyl groups from mono,
di and trimethylated H3K9. Thus, our data suggest that specific gene regulation requires the assembly and coordinate action of demethylases with distinct substrate specificities. Access
through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices
may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support
SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS CHROMATIN BINDING OF FOXA1 IS PROMOTED BY LSD1-MEDIATED DEMETHYLATION IN PROSTATE CANCER Article 31 August 2020 A CARBOXY-TERMINAL UBIQUITYLATION SITE
REGULATES ANDROGEN RECEPTOR ACTIVITY Article Open access 05 January 2024 PIM1 PHOSPHORYLATION OF THE ANDROGEN RECEPTOR AND 14-3-3 Ζ REGULATES GENE TRANSCRIPTION IN PROSTATE CANCER Article
Open access 25 October 2021 REFERENCES * Strahl, B. D. & Allis, C. D. The language of covalent histone modifications. _Nature_ 403, 41–45 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Shi, Y.
et al. Histone demethylation mediated by the nuclear amine oxidase homolog LSD1. _Cell_ 119, 941–953 (2004). Article CAS Google Scholar * Metzger, E. et al. LSD1 demethylates repressive
histone marks to promote androgen-receptor-dependent transcription. _Nature_ 437, 436–439 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Tsukada, Y. I. et al. Histone demethylation by a family of
JmjC domain-containing proteins. _Nature_ 435, 811–816 (2005). Article Google Scholar * Whetstine, J. R. et al. Reversal of histone lysine trimethylation by the JMJD2 family of histone
demethylases. _Cell_ 125, 467–481 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar * Cloos, P. A. et al. The putative oncogene GASC1 demethylates tri- and dimethylated lysine 9 on histone H3. _Nature_
442, 307–311 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar * Shi, X. et al. ING2 PHD domain links histone H3 lysine 4 methylation to active gene repression. _Nature_ 442, 96–99 (2006). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Wysocka, J. et al. A PHD finger of NURF couples histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation with chromatin remodelling. _Nature_ 442, 86–90 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Rosenfeld, M. G., Lunyak, V. V. & Glass, C. K. Sensors and signals: a coactivator/corepressor/epigenetic code for integrating signal-dependent programs of transcriptional response.
_Genes Dev._ 20, 1405–1428 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar * Yamane, K. et al. JHDM2A, a JmjC-containing H3K9 demethylase facilitates Transcription activation by androgen receptor.
_Cell_ 125, 483–495 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar * Trewick, S. C., McLaughlin, P. J. & Allshire, R. C. Methylation: lost in hydroxylation? _EMBO Rep._ 6, 315–320 (2005). Article
CAS Google Scholar * Fodor, B. D. et al. Jmjd2b antagonizes H3K9 trimethylation at pericentric heterochromatin in mammalian cells. _Genes Dev._ 20, 1557–1562 (2006). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Klose, R. J. et al. The transcriptional repressor JHDM3A demethylates trimethyl histone H3 lysine 9 and lysine 36. _Nature_ 442, 312–316 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Trojer, P. & Reinberg, D. Histone lysine demethylases and their impact on epigenetics. _Cell_ 125, 213–217 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar * Kang, Z., Pirskanen, A., Janne, O. A.
& Palvimo, J. J. Involvement of proteasome in the dynamic assembly of the androgen receptor transcription complex. _J. Biol. Chem._ 277, 48366–48371 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar
* Metzger, E., Müller, J. M., Ferrari, S., Buettner, R. & Schüle, R. A novel inducible transactivation domain in the androgen receptor: implications for PRK in prostate cancer. _EMBO
J._ 22, 270–280 (2003). Article CAS Google Scholar * Gray, S. G. et al. Functional characterization of JMJD2A, a histone deacetylase- and retinoblastoma-binding protein. _J. Biol. Chem._
280, 28507–28518 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Müller, J. M. et al. The transcriptional coactivator FHL2 transmits Rho signals from the cell membrane into the nucleus. _EMBO J._
21, 736–748 (2002). Article Google Scholar * Müller, J. M. et al. FHL2, a novel tissue-specific coactivator of the androgen receptor. _EMBO J._ 19, 359–369 (2000). Article Google Scholar
* Shang, Y., Myers, M. & Brown, M. Formation of the androgen receptor transcription complex. _Mol. Cell_ 9, 601–610 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar * Wiznerowicz, M. & Trono,
D. Conditional suppression of cellular genes: lentivirus vector-mediated drug-inducible RNA interference. _J. Virol._ 77, 8957–8961 (2003). Article CAS Google Scholar * O'Neill, T.
E., Roberge, M. & Bradbury, E. M. Nucleosome arrays inhibit both initiation and elongation of transcripts by bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. _J. Mol. Biol._ 223, 67–78 (1992). Article
CAS Google Scholar * Rigaut, G. et al. A generic protein purification method for protein complex characterization and proteome exploration. _Nature Biotechnol._ 17, 1030–1032 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank S. Gray for generously providing reagents. We thank K. Fischer, L. Walz, F. Klott and S. Vomstein for excellent
technical assistance. We are obliged to M. Hoffmann and A. Schwentek from the sequencing core facility. We thank M. Follo for help with editing the manuscript. This work was supported by
grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 747/P2, Schu 688/7-1, and Schu 688/9-1), the Dr. Hans Messner-Stiftung, and the Deutsche Krebshilfe (10-2019-Bu I) to R.S. AUTHOR
INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Universitäts-Frauenklinik und Zentrum für Klinische Forschung, Klinikum der Universität Freiburg, Breisacherstrasse 66, Freiburg, 79106, Germany
Melanie Wissmann, Na Yin, Judith M. Müller, Holger Greschik, Thomas Günther, Eric Metzger & Roland Schüle * Research Institute of Molecular Pathology (IMP), The Vienna Biocenter, Dr.
Bohrgasse 7, Vienna, 1030, Austria Barna D. Fodor & Thomas Jenuwein * Max-Planck-Institut für Immunbiologie, Stübeweg 51, Freiburg, 79108, Germany Christine Vogler & Robert Schneider
* Institut für Pathologie, Universitätsklinikum Bonn, Sigmund-Freud-Strasse 25, Bonn, 53127, Germany Reinhard Buettner Authors * Melanie Wissmann View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Na Yin View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Judith M. Müller View author publications You
can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Holger Greschik View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Barna D. Fodor View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Thomas Jenuwein View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Christine
Vogler View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Robert Schneider View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * Thomas Günther View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Reinhard Buettner View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Eric Metzger View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Roland Schüle View author publications You can also search for
this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Roland Schüle. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing financial interests.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary figures S1, S2, S3, S4 and S5 (PDF 194 kb) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS
ARTICLE Wissmann, M., Yin, N., Müller, J. _et al._ Cooperative demethylation by JMJD2C and LSD1 promotes androgen receptor-dependent gene expression. _Nat Cell Biol_ 9, 347–353 (2007).
https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1546 Download citation * Received: 25 October 2006 * Accepted: 02 January 2007 * Published: 04 February 2007 * Issue Date: March 2007 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1546 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently
available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative