An origin of the radio jet in m87 at the location of the central black hole
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
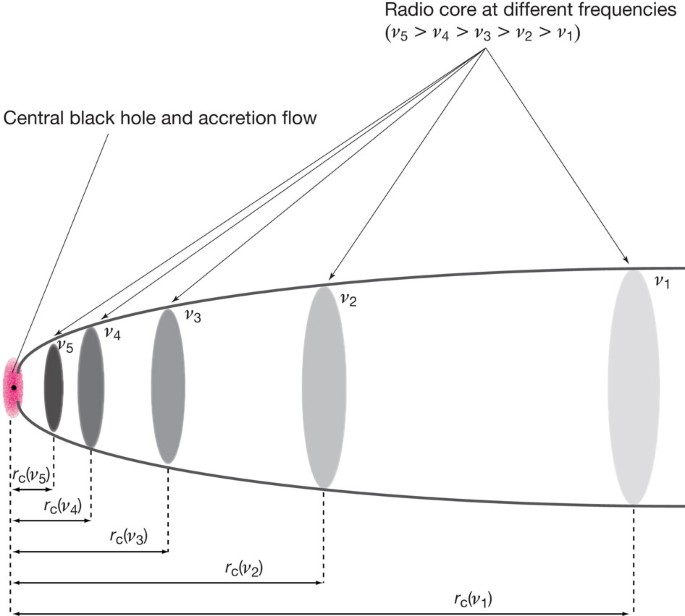
ABSTRACT Powerful radio jets from active galactic nuclei are thought to be powered by the accretion of material onto the supermassive black hole (the ‘central engine’)1,2. M87 is one of the
closest examples of this phenomenon, and the structure of its jet has been probed on a scale of about 100 Schwarzschild radii (_R_s, the radius of the event horizon)3. However, the location
of the central black hole relative to the jet base (a bright compact radio ‘core’) remains elusive4,5. Observations of other jets indicate that the central engines are located about
104–106_R_s upstream from the radio core6,7,8,9. Here we report radio observations of M87 at six frequencies that allow us to achieve a positional accuracy of about 20 microarcseconds. As
the jet base becomes more transparent at higher frequencies, the multifrequency position measurements of the radio core enable us to determine the upstream end of the jet. The data reveal
that the central engine of M87 is located within 14–23_R_s of the radio core at 43 GHz. This implies that the site of material infall onto the black hole and the eventual origin of the jet
reside in the bright compact region seen on the image at 43 GHz. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 51 print issues and online access $199.00 per year only $3.90 per issue Learn more Buy this article *
Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn
about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS PRECESSING JET NOZZLE CONNECTING TO A SPINNING BLACK HOLE IN M87 Article
27 September 2023 COUPLING BETWEEN THE ACCRETING CORONA AND THE RELATIVISTIC JET IN THE MICROQUASAR GRS 1915+105 Article 07 March 2022 ULTRA-HIGH-ENERGY GAMMA-RAY BUBBLE AROUND MICROQUASAR
V4641 SGR Article 16 October 2024 REFERENCES * McKinney, J. C. General relativistic magnetohydrodynamic simulations of the jet formation and large-scale propagation from black hole accretion
systems. _Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc._ 368, 1561–1582 (2006) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Blandford, R. D. & Payne, D. G. Hydromagnetic flows from accretion discs and the
production of radio jets. _Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc._ 199, 883–903 (1982) Article ADS Google Scholar * Junor, W., Biretta, J. A. & Livio, M. Formation of the radio jet in M87 at 100
Schwarzschild radii from the central black hole. _Nature_ 401, 891–892 (1999) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Biretta, J. A., Junor, W. & Livio, M. Evidence for initial jet
formation by an accretion disk in the radio galaxy M87. _New Astron. Rev._ 46, 239–245 (2002) Article ADS Google Scholar * Ly, C., Walker, R. C. & Junor, W. High-frequency VLBI
imaging of the jet base of M87. _Astrophys. J._ 660, 200–205 (2007) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Marscher, A. P. et al. The inner jet of an active galactic nucleus as revealed by a
radio-to-γ-ray outburst. _Nature_ 452, 966–969 (2008) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Marscher, A. P. et al. Probing the inner jet of the quasar PKS 1510−089 with multi-waveband
monitoring during strong gamma-ray activity. _Astrophys. J._ 710, L126–L131 (2010) Article ADS Google Scholar * Agudo, I. et al. Location of γ-ray flare emission in the jet of the BL
Lacertae object OJ 287 more than 14 pc from the central engine. _Astrophys. J._ 726, L13–L18 (2011) Article ADS Google Scholar * Larionov, V. M. et al. Results of WEBT, VLBA and RXTE
monitoring of 3C 279 during 2006–2007. _Astron. Astrophys._ 492, 389–400 (2008) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Blandford, R. D. & Königl, A. Relativistic jets as compact radio
sources. _Astrophys. J._ 232, 34–48 (1979) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Bartel, N., Herring, T. A., Ratner, M. I., Shapiro, I. I. & Corey, B. E. VLBI limits on the proper motion
of the ‘core’ of the superluminal quasar 3C345. _Nature_ 319, 733–738 (1986) Article ADS Google Scholar * Lobanov, A. P. Ultracompact jets in active galactic nuclei. _Astron. Astrophys._
330, 79–89 (1998) ADS Google Scholar * O’Sullivan, S. P. & Gabuzda, D. C. Magnetic field strength and spectral distribution of six parsec-scale active galactic nuclei jets. _Mon. Not.
R. Astron. Soc._ 400, 26–42 (2009) Article ADS Google Scholar * Gebhardt, K. & Thomas, J. The black hole mass, stellar mass-to-light ratio, and dark halo in M87. _Astrophys. J._ 700,
1690–1701 (2009) Article ADS Google Scholar * Jordán, A. et al. The ACS Virgo cluster survey. X. Half-light radii of globular clusters in early-type galaxies: environmental dependencies
and a standard ruler for distance estimation. _Astrophys. J._ 634, 1002–1019 (2005) Article ADS Google Scholar * Königl, A. Relativistic jets as X-ray and gamma-ray sources. _Astrophys.
J._ 243, 700–709 (1981) Article ADS Google Scholar * Kovalev, Y. Y., Lister, M. L., Homan, D. C. & Kellermann, K. I. The inner jet of the radio galaxy M87. _Astrophys. J._ 668,
L27–L30 (2007) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Acciari, V. A. et al. Radio imaging of the very-high-energy γ-ray emission region in the central engine of a radio galaxy. _Science_ 325,
444–448 (2009) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Biretta, J. A., Sparks, W. B. & Macchetto, F. Hubble Space Telescope observations of superluminal motion in the M87 jet. _Astrophys.
J._ 520, 621–626 (1999) Article ADS Google Scholar * Abdo, A. A. et al. A change in the optical polarization associated with a γ-ray flare in the blazar 3C 279. _Nature_ 463, 919–923
(2010) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Ghisellini, G., Tavecchio, F. & Chiaberge, M. Structured jets in TeV BL Lac objects and radiogalaxies. Implications for the observed
properties. _Astron. Astrophys._ 432, 401–410 (2005) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Cheung, C. C., Harris, D. E. & Stawarz, Ł. Superluminal radio features in the M87 jet and the
site of flaring TeV gamma-ray emission. _Astrophys. J._ 663, L65–L68 (2007) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Harris, D. E. et al. in _Extragalactic Jets: Theory and Observation from
Radio to Gamma Ray_ (ASP Conf. Ser. no. 386) (eds Rector, T. A. & De Young, D. S. ) 80–86 (Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 2008) Google Scholar * Chang, C. S., Ros, E., Kovalev, Y.
Y. & Lister, M. L. VLBI detection of the HST-1 feature in the M 87 jet at 2 cm. _Astron. Astrophys._ 515 A38 10.1051/0004-6361/200913915 (2010) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Di
Matteo, T., Allen, S. W., Fabian, A. C., Wilson, A. S. & Young, A. J. Accretion onto the supermassive black hole in M87. _Astrophys. J._ 582, 133–140 (2003) Article ADS Google Scholar
* Yuan, F. Possible evidence for the disc origin for the powering of jets in Sgr A* and nearby elliptical galaxies. _Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc._ 319, 1178–1184 (2000) Article ADS Google
Scholar * Doeleman, S. S. et al. Event-horizon-scale structure in the supermassive black hole candidate at the Galactic Centre. _Nature_ 455, 78–80 (2008) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar
* Broderick, A. E. & Loeb, A. Imaging the black hole silhouette of M87: implications for jet formation and black hole spin. _Astrophys. J._ 697, 1164–1179 (2009) Article ADS Google
Scholar * Takahashi, R. & Mineshige, S. Constraining the size of the dark region around the M87 black hole by space-VLBI observations. _Astrophys. J._ 729, 86–95 (2011) Article ADS
Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank M. Honma, H. Sudou and T. Hirota for discussions about the astrometry analysis; and K. Asada, G. Giovannini, M. Giroletti, M.
Inoue, S. Kameno, S. Koide, S. Sasaki, Ł. Stawarz, N. Sugiyama and N. Yoshida for comments. The Very Long Baseline Array is operated by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory, a facility
of the National Science Foundation, operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc. This work was supported in part by the Graduate University for Advanced Studies
(Sokendai). AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Astronomical Science, The Graduate University for Advanced Studies (SOKENDAI), 2-21-1 Osawa, Mitaka, Tokyo 181-8588,
Japan Kazuhiro Hada, Yoshiaki Hagiwara & Noriyuki Kawaguchi * National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, 2-21-1 Osawa, Mitaka, Tokyo 181-8588, Japan Kazuhiro Hada, Motoki Kino, Hiroshi
Nagai, Yoshiaki Hagiwara & Noriyuki Kawaguchi * Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, 3-1-1 Yoshinodai, Chuo, Sagamihara, Kanagawa 252-5210,
Japan Akihiro Doi & Hiroshi Nagai * Department of Space and Astronautical Science, The Graduate University for Advanced Studies (SOKENDAI), 3-1-1 Yoshinodai, Chuo, Sagamihara, Kanagawa
252-5210, Japan Akihiro Doi Authors * Kazuhiro Hada View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Akihiro Doi View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Motoki Kino View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Hiroshi Nagai View author publications You
can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Yoshiaki Hagiwara View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Noriyuki Kawaguchi View
author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS K.H., A.D. and H.N. designed and proposed the VLBA observations. K.H. led the work and together
with A.D. performed the data analysis. K.H., M.K. and Y.H. jointly wrote the paper. N.K. checked the manuscript. All the authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Kazuhiro Hada. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing financial interests. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY
INFORMATION This file contains Supplementary Methods, Supplementary References, Supplementary Figures 1-5 with legends and Supplementary Tables 1-2. (PDF 3741 kb) POWERPOINT SLIDES
POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR FIG. 1 POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR FIG. 2 POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR FIG. 3 RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Hada, K., Doi, A.,
Kino, M. _et al._ An origin of the radio jet in M87 at the location of the central black hole. _Nature_ 477, 185–187 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10387 Download citation * Received:
31 January 2011 * Accepted: 27 July 2011 * Published: 07 September 2011 * Issue Date: 08 September 2011 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10387 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the
following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer
Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative