Novel activating STAT5B mutations as putative drivers of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
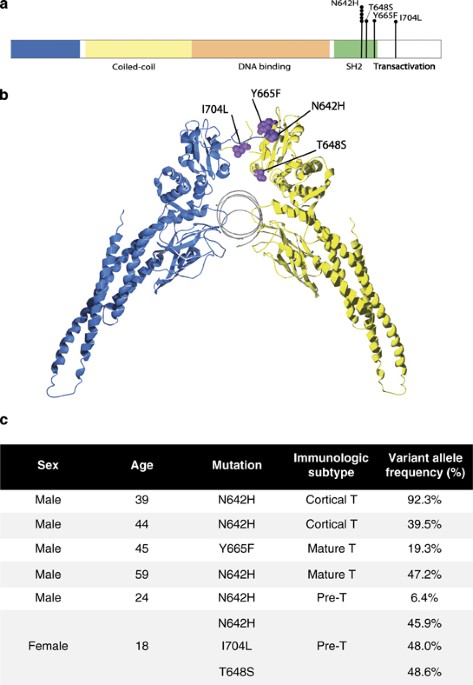
STAT5 has an important role in many hematologic malignancies, but constitutive activation is often a secondary event.1 Mutations to STAT5B and their functional significance were recently
discovered in large granular lymphocytic (LGL) leukemia.2 The mutations located in the SRC homology 2 (SH2) domain of STAT5B lead to constitutive phosphorylation of the mutant protein,
increased transcriptional activity and activation of downstream target genes. However, activating mutations in STAT5B have thus far not been described in other cancers. In T-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL), a complex cooperation of multiple oncogenic aberrations leads to the development of the disease.3 Approximately 9% of childhood T-ALL patients display IL7R
gain-of-function mutations leading to constitutive activation of downstream targets.4 The two main pathways induced by IL7R are PI3K/AKT/MTOR and JAK/STAT5.5 In addition to mutations in
IL7R, somatic JAK1 and JAK3 gain-of-function mutations are relatively prevalent in T-ALL presenting in 10.4% and 7% of adult patients, respectively.6, 7 Activating mutations to IL7R, JAK1,
JAK2 or JAK3 are estimated to occur in 20–30% of all T-ALL patients.8 In naive T cells the stimulation of either JAK–STAT5 or PI3K pathway results in the induction of key anti-apoptotic
factors, including B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) and myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1 (MCL1), while pro-apoptotic BCL-2 family members are inhibited.9 In T-ALL, however, the STAT5 target genes
are inadequately known. Here we report the identification of activating mutations to STAT5B in T-ALL accompanied by overexpression of BCL-XL (BCL2L1) and sensitivity to pan-BCL-2 inhibitors.
Ex vivo drug sensitivity of BM blast cells from the index patient sampled at relapse was assessed against a comprehensive set of 264 approved and investigational drugs representing both
targeted and chemotherapeutic drugs as previously described.11 In short, the drugs were pre-plated in 384-well plates over a 10 000-fold concentration range (for example, 1–10 000 nM), with
10 000 cells added to each well. After a 3-day incubation at 37 °C, cell viability was measured using the CellTiter-Glo reagent (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Dose–response curves for each
drug were generated for the patient cells and BM mononuclear cell fractions from three healthy donors, which served as controls. Results from the assay showed that the index patient blast
cells were sensitive to the pan-BCL-2 family protein inhibitor navitoclax (EC50 81.9 nM) as well as to corticosteroids and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitors (Figure
2c). The blasts did not display sensitivity (EC50 ⩾1 μM) to Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors (ruxolitinib and tofacitinib), RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1) inhibitors
(MK-2220), phosphoinisitide 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitors (for example, idelalisib and XL147), dual inhibitors of PI3K and mammalian target of rapamycin (MTOR) (PF-04691502 and dactolisib) and
rapalogs (temsirolimus and everolimus).
We thank the patients who participated in the study. We acknowledge personnel of the High Throughput Biomedicine Unit and Minna Suvela, Pekka Ellonen, Aino Palva, Pirkko Mattila and Henrikki
Almusa from Institute for Molecular Medicine Finland (FIMM) Technology Centre, University of Helsinki for their expert technical assistance. The Finnish Cancer Societies, Blood Disease
Foundation, Finnish Association of Hematology, Orion-Farmos Research Foundation, Academy of Finland, Finnish Funding Agency for Technology and Innovation, and European Regional Development
Fund supported this work.
M Kontro and H Kuusanmäki: These authors contributed equally to this work.
Department of Medicine, Hematology Research Unit Helsinki, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Central Hospital Cancer Center, Helsinki, Finland
M Kontro, H Kuusanmäki, E I Andersson, H Rajala, S Mustjoki & K Porkka
Institute for Molecular Medicine Finland (FIMM), University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland
H Kuusanmäki, S Eldfors, H Edgren, S Lagström, J M L Martí, M M Majumder, A Parsons, T Pemovska, O Kallioniemi & C A Heckman
Department of Hematology, Oncology, and Tumor Immunology, Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
Department of Clinical Science, Hematology Section, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway
Department of Internal Medicine, Hematology Section, Haukeland University Hospital, Bergen, Norway
Department of Oncology, Hematology and Stem Cell Transplantation, University Hospital Aachen, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany
Department of Clinical Hematology, Turku University Central Hospital, University of Turku, Turku, Finland
Tampere Center for Child Health Research, University of Tampere School of Medicine and Tampere University Hospital, Tampere, Finland
Department of Clinical Chemistry and TYKSLAB, Turku University Central Hospital, University of Turku, Turku, Finland
Division of Hematology-Oncology and Stem Cell Transplantation, Hospital for Children and Adolescents, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland
Institute of Biomedicine, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland
MK and HK designed the study, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript; MK collected most of the sample material; HK performed most of the experiments; SE, HE and JMLM performed sequencing
data analysis; TP and MMM performed drug sensitivity testing and corresponding analysis; EIA, SL, HR, MMM and AP performed the experiments and participated in the data analysis; TB, ØB,
THB, BTG, OL, TL and KV provided the patient specimens and clinical data; and OK, SM, KP and CAH conceived the study, supervised the work and wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to
and approved the final manuscript.
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: