Pulmonary hypertension in preterm infants: results of a prospective screening program
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
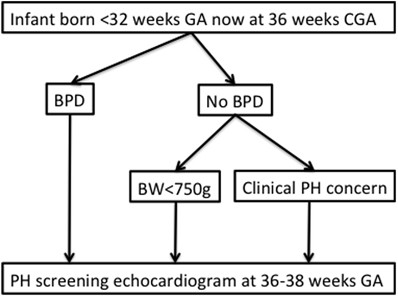
ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: Determine prevalence and associations with pulmonary hypertension (PH) in preterm infants. STUDY DESIGN: Prospective institutional echocardiographic PH screening at 36 to
38 weeks’ corrected gestational age (GA) for infants born <32 weeks' GA who had bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD; group BPD), and infants without BPD who had a birth weight (BW)
<750 g, or clinical suspicion for PH (group NoBPD). RESULTS: Two hundred and four infants were screened (GA 25.9±2 weeks, BW 831±286 g). The PH prevalence in group BPD was higher than in
group NoBPD (44/159 (28%) vs 5/45 (11%); _P_=0.028). In group BPD, BW and GA were lower in infants with PH compared with NoPH. Following correction for BW and GA, necrotizing enterocolitis
(NEC), severe intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), atrial septal defect (ASD), and mortality were independently associated with PH in infants with BPD. In group NoBPD, NEC was the only
identified factor associated with PH. Altogether, screening only those infants with NEC and infants with BPD who also had a BW <840 g would have yielded a 84% sensitivity for detecting
PH, and reduced the number of screening echocardiograms by 43%. CONCLUSIONS: PH in prematurity is associated with NEC in infants with and without BPD. In infants with BPD, smaller GA and BW,
severe IVH, ASD and mortality are also associated with PH. Infants without identified PH-associated factors may not require routine echocardiographic PH screening. Access through your
institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print
issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to
local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT
BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS EARLY PULMONARY HYPERTENSION IS A RISK FACTOR FOR BRONCHOPULMONARY DYSPLASIA-ASSOCIATED LATE PULMONARY HYPERTENSION IN EXTREMELY PRETERM INFANTS Article Open access 27
May 2021 ASSOCIATION OF THE RESPIRATORY SEVERITY SCORE WITH BRONCHOPULMONARY DYSPLASIA-ASSOCIATED PULMONARY HYPERTENSION IN INFANTS BORN EXTREMELY PRETERM Article 18 October 2023 PDA
MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES AND PULMONARY HYPERTENSION IN EXTREME PRETERM INFANTS WITH BRONCHOPULMONARY DYSPLASIA Article 19 June 2024 REFERENCES * Ambalavanan N, Mourani P . Pulmonary
hypertension in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. _Birth Defects Res A_ 2014; 100 (3): 240–246. Article CAS Google Scholar * Mourani PM, Ivy DD, Gao D, Abman SH . Pulmonary vascular effects of
inhaled nitric oxide and oxygen tension in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. _Am J Respir Crit Care Med_ 2004; 170 (9): 1006–1013. Article PubMed Google Scholar * An HS, Bae EJ, Kim GB, Kwon
BS, Beak JS, Kim EK _et al_. Pulmonary hypertension in preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. _Korean Circ J_ 2010; 40 (3): 131–136. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
* Ali Z, Schmidt P, Dodd J, Jeppesen DL . Predictors of bronchopulmonary dysplasia and pulmonary hypertension in newborn children. _Dan Med J_ 2013; 60 (8): A4688. PubMed Google Scholar
* Slaughter JL, Pakrashi T, Jones DE, South AP, Shah TA . Echocardiographic detection of pulmonary hypertension in extremely low birth weight infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
requiring prolonged positive pressure ventilation. _J Perinatol_ 2011; 31 (10): 635–640. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kim GB . Pulmonary hypertension in infants with
bronchopulmonary dysplasia. _Korean J Pediatr_ 2010; 53 (6): 688–693. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Bhat R, Salas AA, Foster C, Carlo WA, Ambalavanan N . Prospective
analysis of pulmonary hypertension in extremely low birth weight infants. _Pediatrics_ 2012; 129 (3): e682–e689. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Mirza H, Ziegler J, Ford
S, Padbury J, Tucker R, Laptook A . Pulmonary hypertension in preterm infants: prevalence and association with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. _J Pediatr_ 2014; 165 (5): 909–914 e901. Article
PubMed Google Scholar * Mourani PM, Sontag MK, Younoszai A, Miller JI, Kinsella JP, Baker CD _et al_. Early pulmonary vascular disease in preterm infants at risk for bronchopulmonary
dysplasia. _Am J Respir Crit Care Med_ 2015; 191 (1): 87–95. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Khemani E, McElhinney DB, Rhein L, Andrade O, Lacro RV, Thomas KC _et al_.
Pulmonary artery hypertension in formerly premature infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: clinical features and outcomes in the surfactant era. _Pediatrics_ 2007; 120 (6): 1260–1269.
Article PubMed Google Scholar * Stuart BD, Sekar P, Coulson JD, Choi SE, McGrath-Morrow SA, Collaco JM . Health-care utilization and respiratory morbidities in preterm infants with
pulmonary hypertension. _J Perinatol_ 2013; 33 (7): 543–547. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Check J, Gotteiner N, Liu X, Su E, Porta N, Steinhorn R _et al_. Fetal growth restriction
and pulmonary hypertension in premature infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. _J Perinatol_ 2013; 33 (7): 553–557. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Ehrenkranz RA,
Walsh MC, Vohr BR, Jobe AH, Wright LL, Fanaroff AA _et al_. Validation of the National Institutes of Health consensus definition of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. _Pediatrics_ 2005; 116 (6):
1353–1360. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Bizzarro MJ, Raskind C, Baltimore RS, Gallagher PG . Seventy-five years of neonatal sepsis at Yale: 1928–2003. _Pediatrics_ 2005; 116 (3):
595–602. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Garner JS, Jarvis WR, Emori TG, Horan TC, Hughes JM . CDC definitions for nosocomial infections, 1988. _Am J Infect Control_ 1988; 16 (3):
128–140. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kliegman RM, Walsh MC . Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: pathogenesis, classification, and spectrum of illness. _Curr Probl Pediatr_ 1987;
17 (4): 213–288. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H . Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants
with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. _J Pediatr_ 1978; 92 (4): 529–534. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lai WW, Mertens LL, Cohen MS, Geva T . _Echocardiography in Pediatric and
Congenital Heart Disease_. Blackwell Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. Book Google Scholar * Hoeper MM, Bogaard HJ, Condliffe R, Frantz R, Khanna D, Kurzyna M _et al_. Definitions and
diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension. _J Am Coll Cardiol_ 2013; 62 (25 Suppl): D42–D50. Article PubMed Google Scholar * King ME, Braun H, Goldblatt A, Liberthson R, Weyman AE .
Interventricular septal configuration as a predictor of right ventricular systolic hypertension in children: a cross-sectional echocardiographic study. _Circulation_ 1983; 68 (1): 68–75.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kim DH, Kim HS, Choi CW, Kim EK, Kim BI, Choi JH . Risk factors for pulmonary artery hypertension in preterm infants with moderate or severe
bronchopulmonary dysplasia. _Neonatology_ 2012; 101 (1): 40–46. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Abraham S, Weismann CG . Left ventricular end-systolic eccentricity index for assessment of
pulmonary hypertension in infants. _Echocardiography_ 2016; 33: 910–915. Article PubMed Google Scholar * D'Alto M, Romeo E, Argiento P, Pavelescu A, Melot C, D'Andrea A _et
al_. Echocardiographic prediction of pre- versus postcapillary pulmonary hypertension. _J Am Soc Echocardiogr_ 2015; 28 (1): 108–115. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Haddad F, Guihaire J,
Skhiri M, Denault AY, Mercier O, Al-Halabi S _et al_. Septal curvature is marker of hemodynamic, anatomical, and electromechanical ventricular interdependence in patients with pulmonary
arterial hypertension. _Echocardiography_ 2014; 31 (6): 699–707. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Lopez-Candales A . Determinants of an abnormal septal curvature in chronic pulmonary
hypertension. _Echocardiography_ 2015; 32 (1): 49–55. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Albertini M, Ciminaghi B, Mazzola S, Clement MG . Improvement of respiratory function by bosentan
during endotoxic shock in the pig. _Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids_ 2001; 65 (2): 103–108. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Toney BM, Fisher AJ, Albrecht M, Lockett AD,
Presson RG, Petrache I _et al_. Selective endothelin-A receptor blockade attenuates endotoxin-induced pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular dysfunction. _Pulm Circ_ 2014; 4 (2):
300–310. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Nowicki PT, Caniano DA, Hammond S, Giannone PJ, Besner GE, Reber KM _et al_. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase in human intestine
resected for necrotizing enterocolitis. _J Pediatr_ 2007; 150 (1): 40–45. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Vannemreddy P, Notarianni C, Yanamandra K, Napper D, Bocchini J . Is an
endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene mutation a risk factor in the origin of intraventricular hemorrhage? _Neurosurg Focus_ 2010; 28 (1): E11. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Montgomery
AM, Bazzy-Asaad A, Asnes JD, Bizzarro MJ, Ehrenkranz RA, Weismann CG . Biochemical screening for pulmonary hypertension in preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. _Neonatology_
2016; 109 (3): 190–194. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Tanner K, Sabrine N, Wren C . Cardiovascular malformations among preterm infants. _Pediatrics_ 2005; 116 (6): e833–e838.
Article PubMed Google Scholar * Lammers A, Hager A, Eicken A, Lange R, Hauser M, Hess J . Need for closure of secundum atrial septal defect in infancy. _J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg_ 2005;
129 (6): 1353–1357. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Thomas VC, Vincent R, Raviele A, Diehl H, Qian H, Kim D . Transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defect in infants less than
12 months of age improves symptoms of chronic lung disease. _Congenit Heart Dis_ 2012; 7 (3): 204–211. Article PubMed Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was
supported by the Department of Pediatrics, Yale University School of Medicine. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology,
Section of Pediatric Cardiology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA C G Weismann & J D Asnes * Pediatric Heart Center, Skåne Universitetssjukhus, Lasarettgatan 48,
Lund, Sweden C G Weismann * Department of Pediatrics, Section of Pediatric Respiratory Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA A Bazzy-Asaad & C Tolomeo *
Department of Pediatrics, Section of Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA R A Ehrenkranz & M J Bizzarro Authors * C G Weismann View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * J D Asnes View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * A Bazzy-Asaad View
author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * C Tolomeo View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * R A
Ehrenkranz View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M J Bizzarro View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to C G Weismann. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no conflict of interest. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and
permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Weismann, C., Asnes, J., Bazzy-Asaad, A. _et al._ Pulmonary hypertension in preterm infants: results of a prospective screening program. _J
Perinatol_ 37, 572–577 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2016.255 Download citation * Received: 22 February 2016 * Revised: 02 November 2016 * Accepted: 13 December 2016 * Published: 16
February 2017 * Issue Date: May 2017 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2016.255 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable
link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative