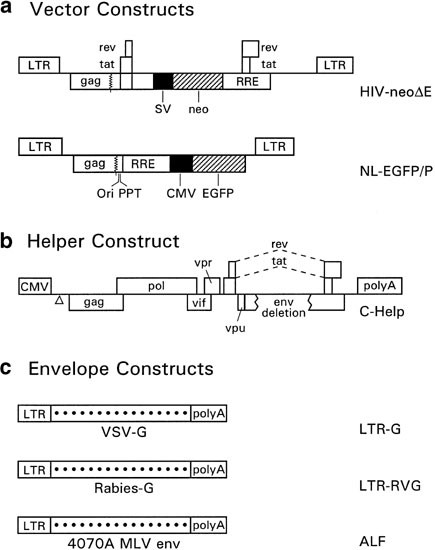
Production and concentration of pseudotyped hiv-1-based gene transfer vectors
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Strategies to generate highly concentrated HIV-1 vector pseudotypes involving different envelope (Env) proteins including the vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) G glycoprotein, the
Moloney murine leukemia virus (MLV) 4070A amphotropic Env and the rabies G glycoprotein were established. Virus stocks were prepared by transient transfection using standard cell culture
media or serum-free media. Such stocks were concentrated 50- to 300-fold by ultracentrifugation or by ultrafiltration using Centricon Plus-80 units yielding titers of up to 10_9_transducing
units per milliliter. There was no loss in titer with any of the pseudotypes tested. Thus, like lentiviral vectors pseudotyped with VSV-G, HIV-1-based vectors pseudotyped with the MLV 4070A
amphotropic Env and the rabies G glycoprotein resist inactivation during concentration. This opens up the possibility to generate highly concentrated HIV-1 vector stocks carrying alternative
Env proteins on a large scale. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your
institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 6 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $43.17 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access
to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our
FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS THE STABILITY OF ENVELOPE-PSEUDOTYPED LENTIVIRAL VECTORS Article Open access 24 September 2020 ENGINEERED CHO CELLS AS
A NOVEL AAV PRODUCTION PLATFORM FOR GENE THERAPY DELIVERY Article Open access 06 November 2023 AN EFFICIENT PLASMID-BASED SYSTEM FOR THE RECOVERY OF RECOMBINANT VESICULAR STOMATITIS VIRUS
ENCODING FOREIGN GLYCOPROTEINS Article Open access 25 June 2024 REFERENCES * Naldini L . Lentiviruses as gene transfer agents for delivery to non-dividing cells _Curr Opin Biotechnol_ 1998
9: 457–463 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Naldini L, Verma IM . Lentiviral vectors. In: Friedmann T (ed) _The Development of Human Gene Therapy_ Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press:
Cold Spring Harbor 1999 47–60 Google Scholar * Naldini L _et al_. In vivo gene delivery and stable transduction of nondividing cells by a lentiviral vector _Science_ 1996 272: 263–267
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bartz SR, Rogel ME, Emerman M . Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 cell cycle control: Vpr is cytostatic and mediates G2 accumulation by a mechanism
which differs from DNA damage checkpoint control _J Virol_ 1996 70: 2324–2331 CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Burns JC _et al_. Vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein
pseudotyped retroviral vectors: concentration to very high titer and efficient gene transfer into mammalian and nonmammalian cells _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 1993 90: 8033–8037 Article CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Reiser J _et al_. Transduction of nondividing cells using pseudotyped defective high-titer HIV type 1 particles _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 1996 93:
15266–15271 Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Mochizuki H _et al_. High-titer immunodeficiency type 1-based vector systems for gene delivery into nondividing cells _J
Virol_ 1998 72: 8873–8883 CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Cosset FL _et al_. High-titer packaging cells producing recombinant retroviruses resistant to human serum _J Virol_
1995 69: 7430–7436 CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chu TH, Dornburg R . Toward highly efficient cell-type-specific gene transfer with retroviral vectors displaying
single-chain antibodies _J Virol_ 1997 71: 720–725 CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * DuBridge RB _et al_. Analysis of mutation in human cells by using an Epstein–Barr virus
shuttle system _Mol Cell Biol_ 1987 7: 379–387 Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Pear WS, Nolan GP, Scott ML, Baltimore D . Production of high-titer helper-free
retroviruses by transient transfection _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 1993 90: 8392–8396 Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Charneau P _et al_. HIV-1 reverse transcription. A
termination step at the center of the genome _J Mol Biol_ 1994 241: 651–662 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS I am grateful to Yasuhiro Takeuchi for
providing plasmid ALF. I thank Simon Tang and Hideki Mochizuki for their help during the early phase of this work. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Developmental and Metabolic
Neurology Branch, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD J Reiser * Louisiana State University Gene Therapy Program, Louisiana
State University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, USA J Reiser Authors * J Reiser View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar RIGHTS AND
PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Reiser, J. Production and concentration of pseudotyped HIV-1-based gene transfer vectors. _Gene Ther_ 7, 910–913
(2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301188 Download citation * Received: 02 September 1999 * Accepted: 15 February 2000 * Published: 25 May 2000 * Issue Date: 01 June 2000 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301188 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * lentiviral vectors * pseudotypes * gene therapy