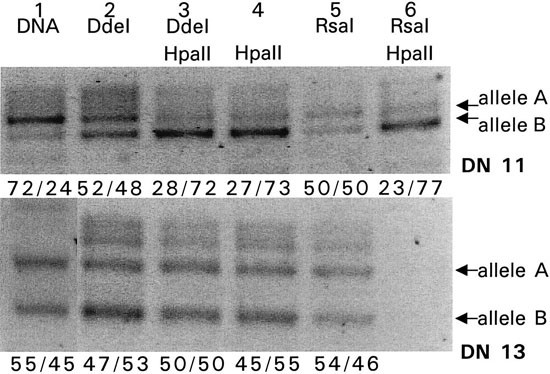
Acquired skewing of lyonization remains stable for a prolonged period in healthy blood donors
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT The pattern of X-chromosome inactivation (XCIP), or Lyonization, can be used to distinguish monoclonal from polyclonal cell populations in females. However, a skewed XCIP exists in
hematopoietic cells in approximately 40% of healthy elderly females, interfering with interpretation of clonality assays. In hematopoiesis, an active stem cell pool is assumed to be present
within a larger population of inactive stem cells, with a continuous exchange of cells between the two compartments. The assumption that the active stem cell pool size decreases with age may
explain the phenomenon of acquired skewing occurring by chance and predicts the XCIP of this population to fluctuate. This fluctuation should be reflected in the XCIP of peripheral
granulocytes. We examined the XCIP for fluctuations in time in peripheral granulocytes, monocytes and T cells of young, middle-aged and elderly healthy females. We used an optimized HUMARA
PCR assay that eliminates unbalanced DNA amplification. We found no fluctuations in XCIP in any age group in up to 18 months follow-up. We conclude that acquired skewing arises gradually in
life without fluctuations in XCIP and that analysis at multiple time points cannot distinguish monoclonal hematopoiesis from normal, skewed hematopoiesis. Access through your institution Buy
or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and
online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes
which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY
OTHERS SKEWNESS OF X-CHROMOSOME INACTIVATION INCREASES WITH AGE AND VARIES ACROSS BIRTH COHORTS IN ELDERLY DANISH WOMEN Article Open access 22 February 2021 DISTINCTION OF LYMPHOID AND
MYELOID CLONAL HEMATOPOIESIS Article 18 October 2021 SHARED AND DISTINCT GENETIC ETIOLOGIES FOR DIFFERENT TYPES OF CLONAL HEMATOPOIESIS Article Open access 08 September 2023 REFERENCES *
Lyon MF . Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (_mus musculus_ L.) _Nature_ 1961 190: 372–373 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Vogelstein B, Fearon ER, Hamilton SR, Feinberg
AP . Use of restriction fragment length polymorphisms to determine the clonal origin of human tumors _Science_ 1985 227: 642–645 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gale RE, Wainscoat JS
. Clonal analysis using X-linked DNA polymorphisms _Br J Haematol_ 1993 85: 2–8 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Allen RC, Zoghbi HY, Moseley AB, Rosenblatt HM, Belmont JW .
Methylation of _Hpa_II and _Hha_I sites near the polymorphic CAG repeat in the human androgen-receptor gene correlates with X chromosome inactivation _Am J Hum Genet_ 1992 51: 1229–1239 CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Mutter GL, Boynton KA . PCR bias in amplification of androgen receptor alleles, a trinucleotide repeat marker used in clonality studies _Nucleic
Acids Res_ 1995 23: 1411–1418 Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Gale RE, Mein CA, Linch DC . Quantification of X-chromosome inactivation patterns in haematological
samples using the DNA PCR-based HUMARA assay _Leukemia_ 1996 10: 362–367 CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Busque L, Mio R, Mattioli J, Brais E, Blais N, Lalonde Y, Maragh M, Gilliland DG .
Nonrandom X-inactivation patterns in normal females: lyonization ratios vary with age _Blood_ 1996 88: 59–65 CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Champion KM, Gilbert JG, Asimakopoulos FA,
Hinshelwood S, Green AR . Clonal haemopoiesis in normal elderly women: implications for the myeloproliferative disorders and myelodysplastic syndromes _Br J Haematol_ 1997 97: 920–926
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gale RE, Fielding AK, Harrison CN, Linch DC . Acquired skewing of X-chromosome inactivation patterns in myeloid cells of the elderly suggests
stochastic clonal loss with age _Br J Haematol_ 1997 98: 512–519 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Tonon L, Bergamaschi G, Dellavecchia C, Rosti V, Lucotti C, Malabarba L, Novella A,
Vercesi E, Frassoni F, Cazzola M . Unbalanced X-chromosome inactivation in haemopoietic cells from normal women _Br J Haematol_ 1998 102: 996–1003 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Nakahara Y, Suzuki H, Ohashi H, Hatano S, Tomita A, Kinoshita T, Murate T, Saito H, Hotta T . Clonality analysis of granulocytes and T lymphocytes in healthy females by the PCR-based HUMARA
method _Int J Hematol_ 1999 69: 237–243 CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wiggans RG, Jacobson RJ, Fialkow PJ, Woolley PV, Macdonald JS, Schein PS . Probable clonal origin of acute myeloblastic
leukemia following radiation and chemotherapy of colon cancer _Blood_ 1978 52: 659–663 CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gale RE, Bunch C, Moir DJ, Patterson KG, Goldstone AH, Linch DC .
Demonstration of developing myelodysplasia/acute myeloid leukaemia in haematologically normal patients after high-dose chemotherapy and autologous bone marrow transplantation using
X-chromosome inactivation patterns _Br J Haematol_ 1996 93: 53–58 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Fialkow PJ, Faguet GB, Jacobson RJ, Vaidya K, Murphy S . Evidence that essential
thrombocythemia is a clonal disorder with origin in a multipotent stem cell _Blood_ 1981 58: 916–919 CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Anger B, Janssen JW, Schrezenmeier H, Hehlmann R, Heimpel
H, Bartram CR . Clonal analysis of chronic myeloproliferative disorders using X-linked DNA polymorphisms _Leukemia_ 1990 4: 258–261 CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Cheshier SH, Morrison SJ,
Liao X, Weissman IL . _In vivo_ proliferation and cell cycle kinetics of long-term self-renewing hematopoietic stem cells _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 1999 96: 3120–3125 Article CAS PubMed
PubMed Central Google Scholar * Abkowitz JL, Golinelli D, Harrison DE, Guttorp P . _In vivo_ kinetics of murine hemopoietic stem cells _Blood_ 2000 96: 3399–3405 CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Wang JC, Doedens M, Dick JE . Primitive human hematopoietic cells are enriched in cord blood compared with adult bone marrow or mobilized peripheral blood as measured by the
quantitative _in vivo_ SCID-repopulating cell assay _Blood_ 1997 89: 3919–3924 CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Abkowitz JL, Taboada M, Shelton GH, Catlin SN, Guttorp P, Kiklevich JV . An X
chromosome gene regulates hematopoietic stem cell kinetics _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 1998 95: 3862–3866 Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Christensen K, Kristiansen M,
Hagen-Larsen H, Skytthe A, Bathum L, Jeune B, Andersen-Ranberg K, Vaupel JW, Orstavik KH . X-linked genetic factors regulate hematopoietic stem-cell kinetics in females _Blood_ 2000 95:
2449–2451 CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Vickers MA, McLeod E, Spector TD, Wilson IJ . Assessment of mechanism of acquired skewed X inactivation by analysis of twins _Blood_ 2001 97:
1274–1281 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was supported by a grant from the Dutch Cancer Society (NKB). AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND
AFFILIATIONS * Central Hematology Laboratory, University Medical Center Nijmegen, Nijmegen, The Netherlands JP van Dijk, L Heuver, E Stevens-Linders, JH Jansen & EJBM Mensink *
Department of Hematology, University Medical Center Nijmegen, Nijmegen, The Netherlands RAP Raymakers & T de Witte Authors * JP van Dijk View author publications You can also search for
this author inPubMed Google Scholar * L Heuver View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * E Stevens-Linders View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * JH Jansen View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * EJBM Mensink View author publications You
can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * RAP Raymakers View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * T de Witte View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE van Dijk, J., Heuver, L.,
Stevens-Linders, E. _et al._ Acquired skewing of Lyonization remains stable for a prolonged period in healthy blood donors. _Leukemia_ 16, 362–367 (2002).
https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402379 Download citation * Received: 15 June 2001 * Accepted: 14 November 2001 * Published: 04 March 2002 * Issue Date: 01 March 2002 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402379 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * hematopoiesis * Lyonization * skewing * HUMARA