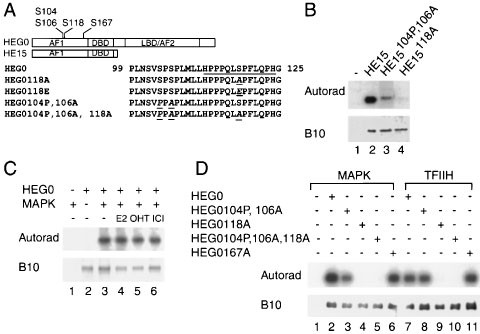
Phosphorylation of human estrogen receptor α at serine 118 by two distinct signal transduction pathways revealed by phosphorylation-specific antisera
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
Estrogen receptor α (ERα) is a transcription factor that regulates expression of target genes in a ligand-dependent manner. Activation of gene expression is mediated by two transcription
activation functions AF-1 and AF-2, which act in a promoter- and cell-specific manner. Whilst AF-2 activity is regulated by estrogen (E2) binding, the activity of AF-1 is additionally
modulated by phosphorylation at several sites. One of these phosphorylation sites, serine 118 (S118) is of particular interest as its mutation significantly reduces ERα activity. Previous
studies have shown that S118 can be phosphorylated by the ERK1/2 mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPK) and by the cyclin-dependent protein kinase Cdk7. In this study we use antisera that
specifically recognize ERα phosphorylated at S118 to demonstrate that MAPK phosphorylates S118 in a ligand-independent manner, whereas Cdk7 mediates E2-induced phosphorylation of S118. E2
stimulation of S118 phosphorylation was observed within 10 min of its addition and was maximal at 10−7 M E2. S118 phosphorylation was maximal at 30 min but then declined, such that by 180
min following E2 addition little S118 phosphorylation was evident. S118 phosphorylation was also induced by the partial estrogen antagonist 4-hydroxytamoxifen, but not by the complete
antagonist ICI 182, 780. S118 phosphorylation upon addition of the MAPK inducers EGF or PMA followed the expected time courses. Finally, we show that ERα is phosphorylated at S118 in vivo
using immunoblotting of extracts prepared from a series of ERα-positive breast tumours.
We are grateful to Prof Pierre Chambon and Dr Daniel Metzger for the ER plasmids and for expression vectors. We would also like to thank Prof Chris Marshall for providing purified ERK2
protein and plasmids and for helpful discussions. Our thanks also go to Drs S Keyse, E Nigg, T Makela, DO Morgan, G Peters and MH Cobb. For technical help we thank Xiaomei Ouyang. This work
was supported by the Cancer Research UK and the Mandeville Trust.
Present address: PNAC, MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Hills Road, Cambridge, CB2 2QH, UK
Present address: Division of Medical Sciences, National Cancer Centre, Singapore
Department of Cancer Medicine, Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, Hammersmith Hospital Campus, Du Cane Road, London, W12 0NN, UK
Dongsheng Chen, Elinor Washbrook, Naveed Sarwar, Paul E Pace, Vatsala Thirunuvakkarasu, Jacqueline Taylor, Richard J Epstein, R Charles Coombes & Simak Ali
Department of Molecular & Cellular Pathology, University of Dundee, Ninewells Hospital & Medical School, Dundee, DD1 9SY, UK
Institut de Genetique et de Biologie Moleculaire et Cellulaire, Université Louis Pasteur, BP 163, Illkirch Cedex Strasbourg, F-67404, France
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: